The keto diet can be harmful for some individuals, particularly if not followed correctly or without proper medical guidance. While it offers benefits like weight loss and improved energy levels for many, it can also lead to negative health effects, especially for those with certain pre-existing conditions. In this article, we will explore the potential harms of the keto diet, its effects on different populations, and how to approach it safely.
Understanding the Keto Diet

The ketogenic diet, commonly referred to as the keto diet, emphasizes a high-fat, moderate-protein, and very low-carbohydrate intake. By drastically reducing carbohydrate consumption, the body enters a metabolic state called ketosis, where it shifts from using glucose as its primary fuel source to burning fat for energy. This process can lead to rapid weight loss, increased energy levels, and improved mental clarity, which are often cited as reasons for adopting this diet. However, the specific macronutrient ratios can vary, with a typical keto diet consisting of about 70-80% fat, 15-20% protein, and only 5-10% carbohydrates. Understanding these fundamentals is crucial for anyone considering this dietary approach, as the balance of nutrients can significantly impact both health outcomes and overall well-being.
Potential Health Risks of the Keto Diet
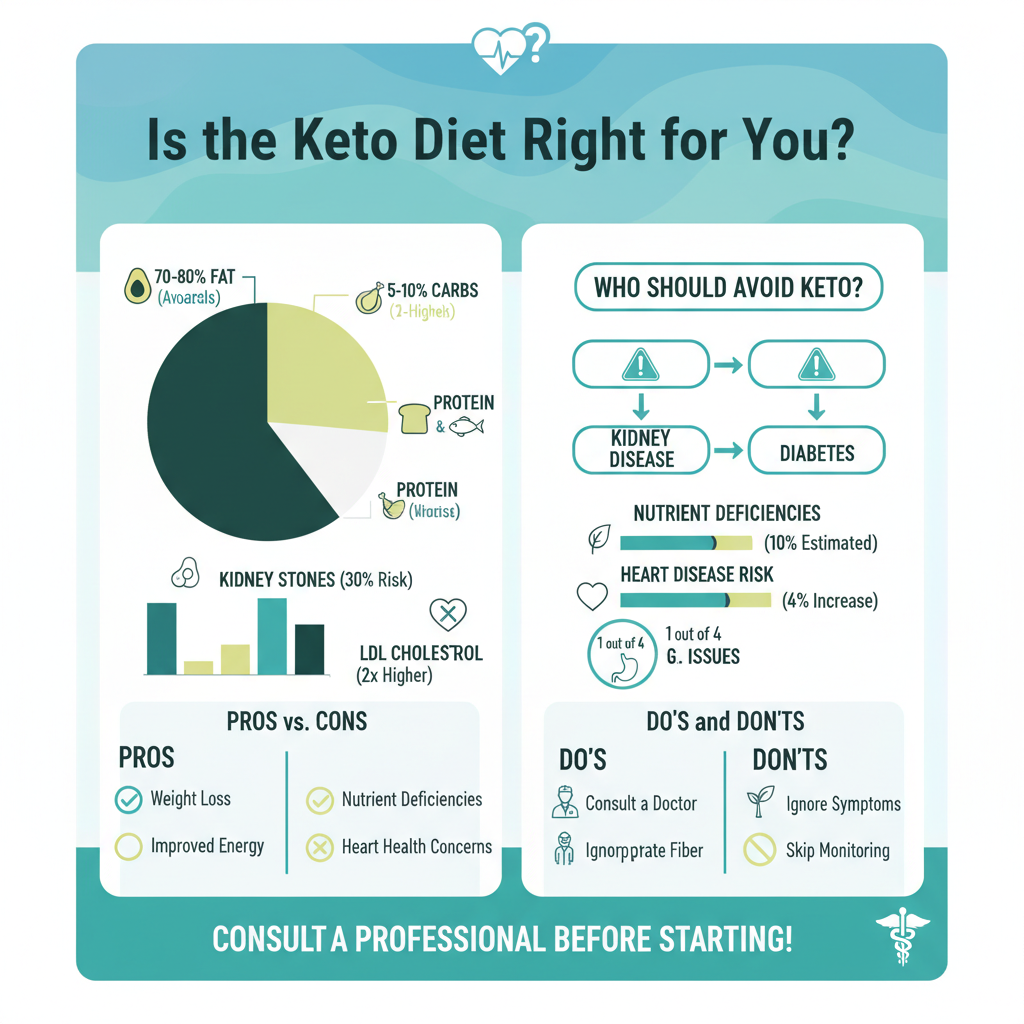

While the keto diet can provide numerous benefits, it is essential to be aware of the potential health risks it entails. One significant concern is the risk of nutrient deficiencies. By eliminating or drastically reducing carbohydrate-rich foods like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, individuals may miss out on essential vitamins, minerals, and fiber, which can lead to complications over time. For instance, inadequate intake of dietary fiber can result in gastrointestinal issues, including constipation and bloating.
Additionally, the high intake of saturated fats, often found in fatty cuts of meat, butter, and full-fat dairy products, raises concerns about heart health. Research has shown that high levels of saturated fat can elevate LDL cholesterol, a known risk factor for cardiovascular diseases. Moreover, some studies suggest that individuals on a keto diet may be at an increased risk for kidney stones and liver problems, particularly if they have pre-existing conditions affecting these organs.
Who Should Avoid the Keto Diet?
Certain populations should approach the keto diet with caution or avoid it altogether. Individuals with kidney disease are particularly at risk, as the higher protein intake associated with this diet can place additional strain on the kidneys. For those with diabetes, particularly type 1 diabetes, careful monitoring of blood sugar levels is critical, as the keto diet can cause fluctuations that may lead to hypoglycemia or other complications. Furthermore, pregnant or breastfeeding women should also be cautious, as their nutritional needs are heightened, and a restrictive diet may not provide sufficient nourishment for both mother and child.
Individuals with a history of eating disorders may find the restrictive nature of the keto diet triggering, as it may lead to unhealthy relationships with food or exacerbate existing mental health issues. Thus, anyone considering this diet should assess their personal health history and consult a healthcare provider to ensure it is a suitable option.
Short-term vs. Long-term Effects
The keto diet is often touted for its short-term benefits, which can include significant weight loss, enhanced mental clarity, and improved energy levels. Many individuals report feeling more focused and less prone to energy crashes commonly associated with high-carb diets. However, these benefits can come at a price, and long-term adherence to the keto diet can lead to complications that may outweigh its initial advantages.
Long-term effects may include gastrointestinal issues, such as diarrhea or constipation, due to a lack of fiber-rich foods. Additionally, research has indicated that prolonged adherence to a keto diet may result in adverse effects on liver health, as the increased fat intake can lead to fatty liver disease in susceptible individuals. There are also concerns about potential impacts on bone health, as certain nutrients critical for bone density may be lacking in a restrictive diet. Therefore, while short-term improvements may be appealing, the long-term consequences warrant careful consideration.
How to Approach the Keto Diet Safely
For those who decide to pursue the keto diet, a cautious and informed approach is necessary to mitigate potential risks. First and foremost, consulting with a healthcare provider or a registered dietitian is essential. They can provide personalized guidance based on individual health needs and goals, ensuring that the diet is tailored appropriately.
Focusing on whole foods is crucial when following a ketogenic diet. Emphasizing high-quality fats, such as avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil, while incorporating lean proteins and low-carbohydrate vegetables can help create a balanced meal plan. Additionally, considering supplementation may be beneficial to prevent nutrient deficiencies; for instance, a fiber supplement can aid digestive health, and multivitamins can help cover any gaps in essential nutrients.
Monitoring your body’s response to the diet is also important. Keeping track of how you feel physically and mentally can help identify any negative side effects early on, allowing for adjustments as needed.
Alternatives to the Keto Diet
For those who find the keto diet unsuitable or unsustainable, there are alternative dietary approaches that can provide similar benefits without the associated risks. The Mediterranean diet, for example, emphasizes whole grains, healthy fats, lean proteins, and plenty of fruits and vegetables. This approach not only supports weight loss but also promotes heart health and reduces the risk of chronic diseases.
Balanced diets that include a variety of food groups can also lead to weight loss and improved overall health. Incorporating principles from intuitive eating, such as listening to hunger cues and focusing on food quality rather than strict macronutrient ratios, can create a more flexible and sustainable approach to nutrition.
Signs You May Need to Stop the Keto Diet
While many individuals may thrive on the keto diet, it is essential to remain vigilant for signs that indicate it may not be the right fit. Persistent fatigue, digestive issues such as diarrhea or constipation, and noticeable signs of nutrient deficiency—such as hair loss or weakened immune function—can signal that the diet is adversely affecting your health.
For individuals with diabetes, uncontrolled blood sugar levels or significant fluctuations should prompt a reevaluation of the diet. Adverse reactions, whether physical or emotional, are also critical indicators that the keto diet might not be suitable. If you experience any of these symptoms, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional and consider modifying or discontinuing the diet.
The keto diet has both potential benefits and risks that vary depending on individual health conditions and dietary choices. Understanding these factors is crucial for anyone considering this popular eating plan. If you’re interested in exploring the keto diet, it’s essential to do so mindfully and consult with a healthcare professional to ensure it’s right for you. Balancing the pursuit of weight loss and improved health with safety and nutritional adequacy is key to long-term success.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is the keto diet harmful to your health in the long term?
The long-term effects of the keto diet can vary significantly among individuals. Some studies suggest that while short-term weight loss benefits are evident, potential risks include nutrient deficiencies, liver and kidney problems, and an increased risk of heart disease due to high saturated fat intake. It’s crucial for individuals considering the keto diet to consult with a healthcare professional to evaluate personal health conditions and ensure a balanced approach.
What are the potential side effects of starting a keto diet?
Common side effects of starting a keto diet can include fatigue, headache, irritability, and digestive issues, often referred to as the “keto flu.” These symptoms typically occur as the body adjusts to ketosis, a metabolic state where fat becomes the primary energy source instead of carbohydrates. Staying hydrated and ensuring adequate electrolyte intake can help alleviate these side effects.
How does the keto diet affect cholesterol levels?
The keto diet can impact cholesterol levels differently for each individual. While some people may experience an increase in LDL cholesterol levels, others may see improvements in their HDL cholesterol and overall triglycerides. It’s essential to monitor cholesterol levels regularly and consult with a healthcare provider to assess any potential risks associated with a high-fat diet.
Why do some people experience weight regain after stopping the keto diet?
Weight regain after stopping the keto diet often occurs due to the rapid reintroduction of carbohydrates, which can lead to water retention and increased calorie intake. Additionally, without the strict carbohydrate restriction of the keto diet, individuals may return to previous eating habits, resulting in weight gain. To maintain weight loss, it’s crucial to adopt sustainable eating practices and lifestyle changes beyond the diet.
Which groups of people should avoid the keto diet?
Certain individuals should approach the keto diet with caution or avoid it altogether, including those with pre-existing liver or kidney conditions, pregnant or breastfeeding women, and individuals with a history of eating disorders. People on certain medications, especially those for diabetes, should also consult with their doctor, as the keto diet can significantly affect blood sugar levels and medication efficacy.
References
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6070220/
- https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/keto-diet-harmful
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/nutrition-and-healthy-eating/in-depth/keto-diet/art-20484866
- https://www.webmd.com/diet/what-is-the-keto-diet
- https://www.cdc.gov/healthyweight/assessing/bmi/adult_bmi/index.html
- https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health-topics/obesity
- https://www.eatright.org/health/dietary-guidelines-and-myplate/the-ketogenic-diet-and-its-impact-on-health
- Diet Review: Ketogenic Diet for Weight Loss • The Nutrition Source

