The keto diet can be diabetic friendly when approached correctly, focusing on low-carb and high-fat foods that help manage blood sugar levels. This dietary approach has gained popularity not only for weight loss but also for its potential to assist individuals with diabetes in stabilizing their blood glucose levels. In this article, you will learn how the keto diet impacts diabetes management, what to consider before starting, and tips for making it work effectively for your health.
Understanding the Keto Diet

The ketogenic (keto) diet is a high-fat, moderate-protein, and very low-carbohydrate eating plan that aims to shift the body’s metabolism from burning glucose as its primary energy source to burning fat, a state known as ketosis. The typical macronutrient distribution in a keto diet includes about 70-75% of calories from fats, 20-25% from protein, and only about 5-10% from carbohydrates. This significant reduction in carbohydrate intake forces the body to use fats for energy, thereby reducing the levels of insulin and stabilizing blood sugar levels.
The primary goal of the keto diet is to achieve and maintain ketosis, where the liver converts fat into ketones, which serve as an alternative fuel for the brain and body. For individuals with diabetes, this metabolic shift can have profound implications for blood sugar control and overall health.
How Keto Affects Blood Sugar Levels
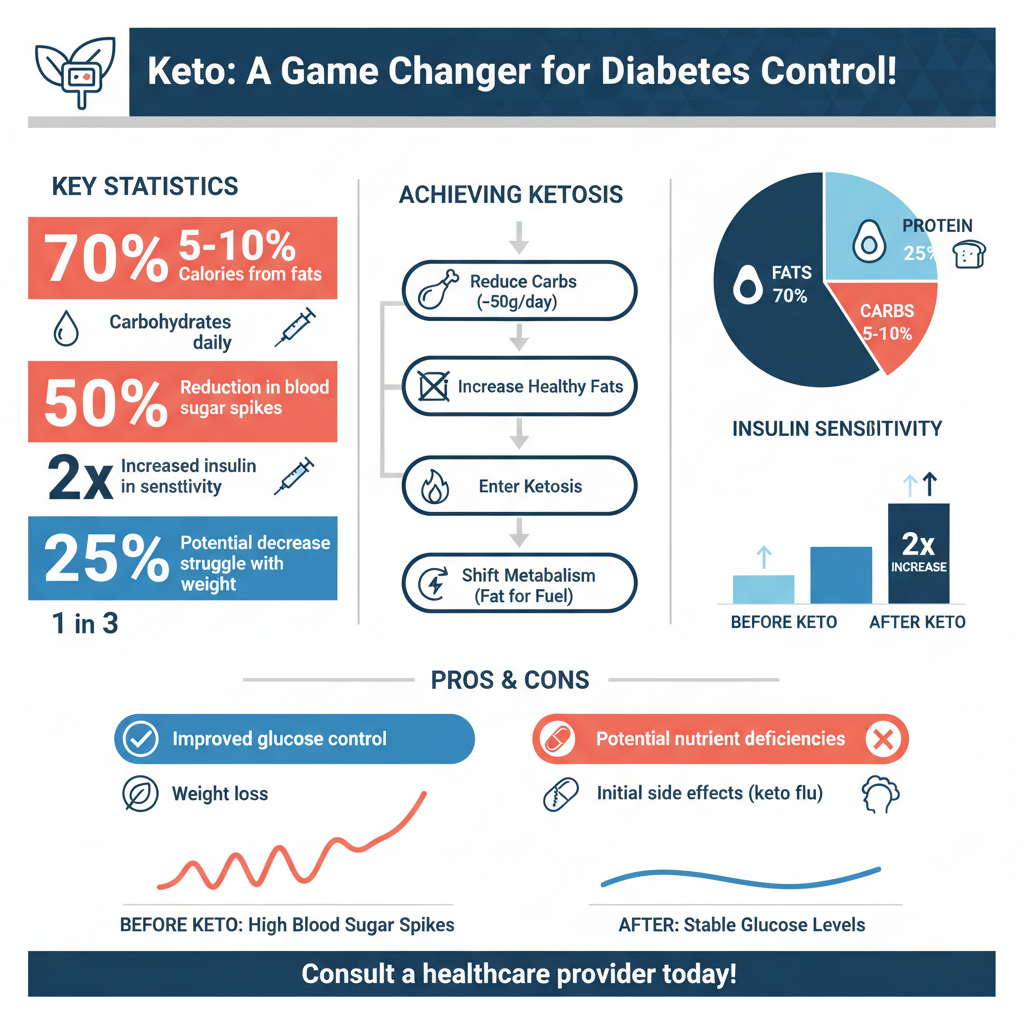

A low-carbohydrate intake, such as that prescribed in the keto diet, can lead to more stable blood sugar levels because carbohydrates are the primary macronutrient that influences glucose spikes. By significantly limiting carbs, individuals can reduce the amount of sugar entering the bloodstream, thereby minimizing the risk of hyperglycemia.
Furthermore, the keto diet can enhance insulin sensitivity, which is particularly beneficial for those with type 2 diabetes. Improved insulin sensitivity means that the body’s cells are better able to utilize insulin, leading to more efficient sugar uptake from the blood. This not only aids in better glucose control but also may reduce the necessary dosage of insulin or other diabetes medications, providing a more manageable approach to diabetes management.
Potential Benefits for Diabetics
The keto diet offers several potential benefits for individuals managing diabetes. One of the most significant advantages is weight management. Excess weight, particularly around the abdomen, is a common issue for many diabetics and can exacerbate insulin resistance. By promoting fat loss and a healthier body composition, the keto diet can help improve metabolic health and enhance diabetes control.
Moreover, some individuals on the keto diet report a reduction in their medication needs. As blood sugar levels stabilize and insulin sensitivity improves, there may be a decreased reliance on diabetes medications, which can lead to potential cost savings and fewer side effects associated with long-term medication use. Additionally, there are anecdotal reports of improved energy levels, better mental clarity, and overall well-being, further supporting the notion that the keto diet can be beneficial for those with diabetes.
Risks and Considerations
Despite the advantages, there are also risks and considerations to keep in mind before starting a keto diet. Some individuals may experience side effects known as the “keto flu,” which can include fatigue, headaches, dizziness, and digestive issues as the body adjusts to a new metabolic state. Additionally, the restrictive nature of the diet may lead to nutrient deficiencies if not properly planned.
It’s crucial to consult a healthcare provider before embarking on the keto diet, particularly for individuals with diabetes. A healthcare professional can help assess individual health needs, provide tailored dietary recommendations, and monitor for any potential complications or contraindications.
Foods to Include and Avoid
To successfully follow a diabetic-friendly keto diet, it is important to focus on foods that promote health and stability in blood sugar levels.
Foods to Include:
– Leafy Greens: Spinach, kale, and collard greens are low in carbs and high in nutrients.
– Healthy Fats: Avocados, olive oil, coconut oil, and nuts are excellent sources of fats that support ketosis.
– Non-Starchy Vegetables: Broccoli, cauliflower, zucchini, and bell peppers are low in carbohydrates and high in fiber.
– Fatty Fish: Salmon, mackerel, and sardines are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which have anti-inflammatory properties.
– Meat and Poultry: Grass-fed beef, chicken, and pork provide high-quality protein without excess carbs.
Foods to Avoid:
– Grains: Bread, pasta, rice, and cereals can spike blood sugar levels and should be avoided.
– Sugars: Added sugars in sweets, sodas, and processed foods can lead to significant glucose spikes.
– Starchy Vegetables: Potatoes, corn, and peas are higher in carbohydrates and can disrupt ketosis.
– Fruits: Most fruits contain higher sugar content; however, berries can be consumed in moderation.
Monitoring and Adjustments
Regular blood sugar monitoring is vital while on the keto diet, as individual responses to dietary changes can vary widely. Continuous glucose monitoring systems or traditional blood glucose meters can help track how the body reacts to different foods and macronutrient ratios.
It is also essential to adjust the diet based on these readings. For instance, if blood sugar levels are consistently low, incorporating small amounts of healthy carbohydrates may be necessary. Conversely, if levels are high, reevaluating fat and protein intake or considering additional carbohydrates might be beneficial. Working closely with a healthcare provider or a registered dietitian can greatly enhance the effectiveness of these adjustments.
Success Stories and Evidence
Research supporting the keto diet as a viable option for diabetes management has been gaining traction. Several studies highlight the positive effects of low-carbohydrate diets on glycemic control and weight management among diabetic populations. For example, a study published in the “Diabetes Therapy” journal showed that participants following a ketogenic diet experienced significant improvements in HbA1c levels, weight loss, and reduced medication requirements over a six-month period.
Anecdotal evidence further reinforces these findings, with numerous individuals sharing their success stories of improved blood sugar levels and overall health after transitioning to a keto lifestyle. Many report feeling more energetic and experiencing fewer diabetes-related complications, which demonstrates the potential of the keto diet in real-world applications.
The keto diet can be a beneficial approach for managing diabetes, provided it is tailored to individual needs and monitored closely. If you’re considering trying the keto diet, consult your healthcare provider for personalized guidance and support. Start your journey toward better blood sugar control today!
Frequently Asked Questions
Is a ketogenic diet safe for people with diabetes?
Yes, a ketogenic diet can be safe for people with diabetes, particularly type 2 diabetes, as it may help improve insulin sensitivity and lower blood sugar levels. However, it’s vital to consult with a healthcare professional before making significant dietary changes. A well-managed ketogenic diet focuses on high-quality fats, moderate protein, and very low carbohydrates, which can lead to better glycemic control for some individuals.
How does the ketogenic diet affect blood sugar levels in diabetics?
The ketogenic diet can lead to more stable blood sugar levels because it minimizes carbohydrate intake, which is the primary macronutrient that raises blood glucose. By reducing carbs, the body switches from glucose to ketones for energy, helping to decrease insulin spikes and improve overall blood sugar management. Nevertheless, monitoring blood sugar levels is crucial, especially during the initial transition to a keto diet.
What foods should diabetics avoid on a ketogenic diet?
Diabetics following a ketogenic diet should avoid high-carb foods such as bread, pasta, rice, sugary snacks, and most fruits. Instead, they should focus on low-carb vegetables (like leafy greens), healthy fats (such as avocados and olive oil), and lean proteins (like chicken and fish). Understanding food labels and carbohydrate counts is essential for effective meal planning on a keto diet.
Which types of ketogenic diets are best for individuals with diabetes?
The best types of ketogenic diets for individuals with diabetes are variations that emphasize whole, nutrient-dense foods while maintaining low carbohydrate levels. The Standard Ketogenic Diet (SKD), which is high in fats (about 70-75% of total calories), moderate in protein (20-25%), and very low in carbohydrates (5-10%), is typically recommended. Additionally, the Targeted Ketogenic Diet (TKD) may benefit those who engage in regular physical activity, allowing for some carbohydrates around workout times.
Why might some diabetics struggle with the ketogenic diet?
Some diabetics may struggle with the ketogenic diet due to the initial adaptation phase known as the “keto flu,” which can include symptoms like fatigue, headaches, and irritability as the body adjusts to burning fat for fuel instead of carbohydrates. Additionally, some individuals may find it challenging to find suitable low-carb foods that meet their nutritional needs or might experience difficulty in managing their diabetes medications alongside dietary changes. It’s essential for those considering keto to work closely with their healthcare provider to tailor the plan to their specific health needs.
References
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6313440/
- https://www.diabetes.org/nutrition/healthy-foods/what-is-the-keto-diet
- https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/basics/diabetes.html
- https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/keto-diet-and-diabetes
- Gluten-free meals: 15 recipes and their health benefits
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6520971/
- https://www.diabetes.co.uk/diet/keto-diet.html
- https://www.nutrition.gov/topics/whats-food/nutrition-keto-diet


