The keto diet can pose risks for certain individuals, especially if not properly managed. While many people experience weight loss and health benefits, it’s crucial to understand the potential dangers associated with this high-fat, low-carb eating plan. In this article, we’ll explore the possible dangers of the keto diet and what you need to consider before starting.
The Basics of the Keto Diet
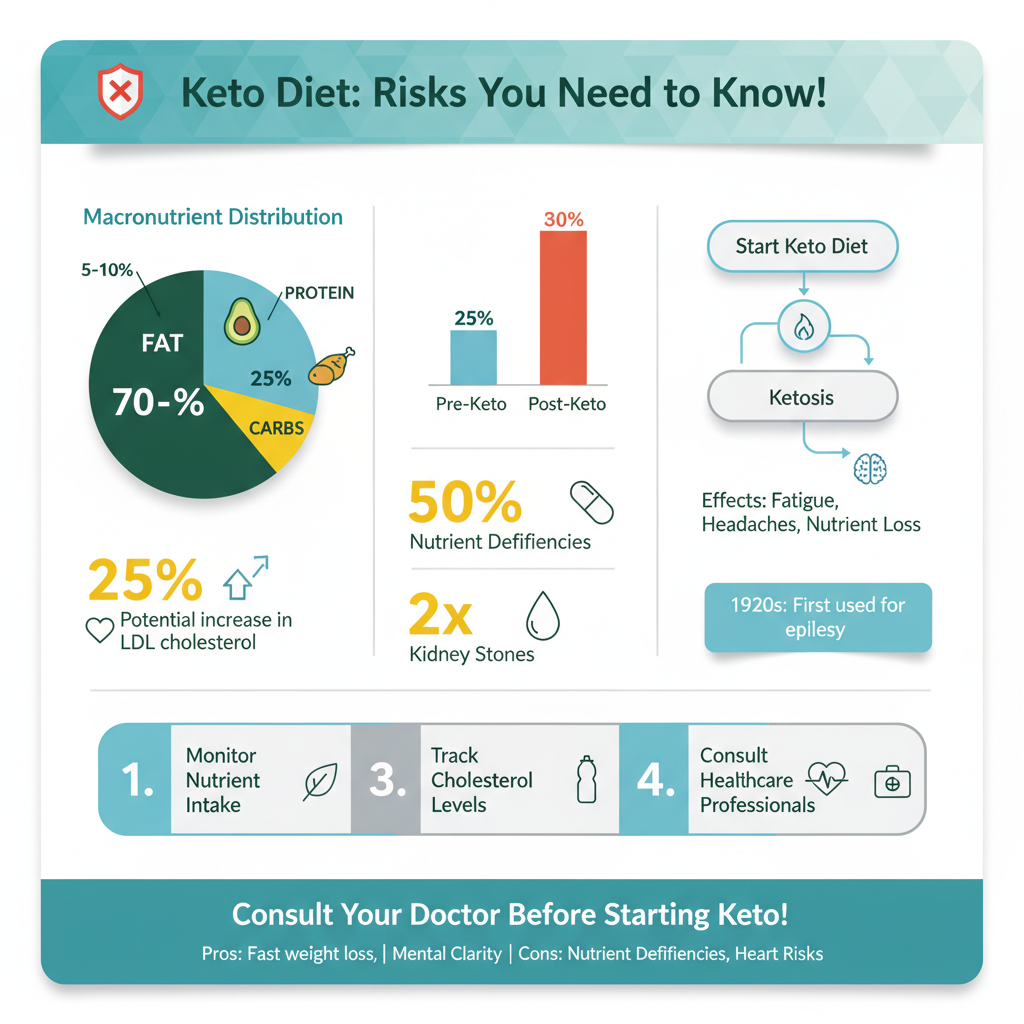

The ketogenic diet involves drastically reducing carbohydrate intake and replacing it with fat. Typically, a standard keto diet consists of approximately 70% to 80% fat, 15% to 25% protein, and a mere 5% to 10% carbohydrates. The goal is to enter a metabolic state known as ketosis, where the body becomes efficient at burning fat for fuel instead of relying on glucose derived from carbohydrates. This shift can lead to quick weight loss and improved energy levels for some individuals; however, the restrictive nature of the diet can also lead to significant challenges.
The keto diet’s history can be traced back to the 1920s when it was first used to treat epilepsy in children. Over the years, it has gained popularity as a weight-loss strategy and for its purported health benefits, including improved blood sugar control and enhanced mental clarity. While these benefits are appealing, understanding the underlying mechanisms and potential pitfalls is essential for anyone considering this dietary approach.
Potential Health Risks
While the keto diet may offer short-term benefits, it is not without its risks. One of the primary concerns is nutrient deficiencies. By limiting food groups, particularly fruits, whole grains, and certain vegetables, individuals may miss out on essential vitamins and minerals crucial for overall health. For instance, inadequate intake of potassium, magnesium, and fiber can lead to a host of health issues, including muscle cramps, fatigue, and digestive problems.
Another significant risk is the increased likelihood of developing kidney stones. The high fat intake, combined with potential dehydration due to a diuretic effect often seen in the initial phases of the diet, can lead to concentrated urine, which increases the likelihood of stone formation. It is essential for individuals on the keto diet to stay adequately hydrated and monitor their body’s response to dietary changes.
Effects on Heart Health
Heart health is a crucial consideration when evaluating the keto diet. One area of concern is cholesterol levels. While some proponents of the diet argue that increased saturated fat can lead to improved HDL cholesterol or “good” cholesterol, others may experience a rise in LDL cholesterol or “bad” cholesterol levels. Elevated LDL cholesterol is a risk factor for heart disease, and individuals with a family history of cardiovascular issues should approach the keto diet with caution.
Additionally, the keto diet can lead to fluctuations in blood pressure, particularly during the initial adaptation phase. As the body shifts from burning carbohydrates to fat for energy, some individuals may experience temporary increases or decreases in blood pressure, leading to feelings of lightheadedness or fatigue. Monitoring blood pressure regularly during this transition is advisable, especially for those with pre-existing conditions.
Impact on Mental Health
The mental health implications of the keto diet cannot be overlooked. Many individuals report experiencing irritability and mood swings, particularly during the initial stages of carbohydrate withdrawal. This emotional fluctuation can be attributed to the brain’s reliance on glucose for optimal function. Reduced carbohydrate intake may lead to decreased serotonin levels, which can contribute to feelings of anxiety and depression.
Furthermore, cognitive function may also be temporarily affected. Although some proponents claim that ketosis can enhance mental clarity and focus, the initial lack of carbohydrates may impair cognitive performance for some individuals. This can manifest as difficulty concentrating, memory lapses, and decreased overall cognitive agility, particularly during the first few weeks of the diet.
Who Should Avoid the Keto Diet?
Certain populations should exercise caution when considering the keto diet. Individuals with pre-existing health conditions, such as liver or pancreas issues, may find the diet contraindicated. The high-fat content can put additional stress on these organs, potentially exacerbating existing health problems. Consulting with a healthcare professional before embarking on the keto journey is essential for those with such conditions.
Pregnant or breastfeeding women should also be wary of the restrictive nature of the keto diet. Proper nutrition is vital during these stages of life to support both maternal health and fetal or infant development. Limiting food groups can hinder the intake of essential nutrients necessary for growth and development. Women in these situations should consider alternative dietary approaches that provide a well-rounded nutritional profile.
Best Practices for a Safer Keto Experience
To minimize the risks associated with the keto diet, it is vital to approach it thoughtfully. Consulting with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian before starting the diet can help ensure it aligns with individual health needs and goals. A tailored approach that considers personal medical history and nutritional requirements is crucial for safely navigating the diet.
Focusing on a balanced intake of nutrients through whole foods can also help mitigate risks. Incorporating a variety of healthy fats, such as olive oil, avocados, and nuts, alongside non-starchy vegetables, can provide essential vitamins and minerals while adhering to keto principles. Regular monitoring of health markers, such as cholesterol levels and blood pressure, is also advisable to track the body’s response to dietary changes.
Alternatives to Consider
For those who are hesitant about the potential risks of the keto diet, various dietary approaches may provide health benefits without the associated risks. The Mediterranean diet, for example, emphasizes whole grains, healthy fats, lean proteins, and plenty of fruits and vegetables. This diet has been linked to numerous health benefits, including improved heart health and reduced inflammation.
Balanced low-carb diets that do not eliminate carbohydrates entirely can also be effective. These diets allow for moderate carbohydrate intake, focusing on quality sources such as whole grains and legumes. This approach can provide the benefits of reduced carbohydrate consumption while still ensuring adequate nutrient intake. Creating a personalized meal plan that incorporates a variety of food groups is essential for overall wellness and can help individuals achieve their health goals without the risks associated with more restrictive diets.
Summarizing the potential dangers of the keto diet is essential for anyone considering this eating plan. While it can lead to weight loss and other benefits, awareness of its risks can help you make informed decisions about your health. If you’re thinking about trying keto, consult with a healthcare provider and consider alternatives that might better suit your lifestyle and health goals. Engaging in a well-balanced approach to nutrition is fundamental to achieving lasting health and wellness.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is the keto diet dangerous for long-term health?
The keto diet can pose risks for long-term health, particularly if not properly managed. Some studies suggest that prolonged adherence to a very low-carb diet may lead to nutrient deficiencies, liver and kidney problems, and increased cholesterol levels. It’s crucial to monitor your health with a healthcare provider and ensure you’re getting a balanced intake of vitamins and minerals while on the keto diet.
What are the potential side effects of starting a keto diet?
Common side effects of starting a keto diet, often referred to as the “keto flu,” include fatigue, nausea, headaches, dizziness, and irritability. These symptoms typically occur as your body adjusts to ketosis, where it shifts from burning carbohydrates to burning fat for energy. Staying hydrated, replenishing electrolytes, and gradually reducing carb intake can help mitigate these side effects.
How can I ensure the keto diet is safe for me?
To ensure the keto diet is safe, consult with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian before starting. They can help you assess your individual health needs and any underlying conditions that may be affected by a low-carb diet. Regular health check-ups during the diet can also help monitor your progress and any potential risks.
Why do some experts consider the keto diet unsafe?
Some experts consider the keto diet unsafe due to its restrictive nature and potential health risks. Concerns include the possibility of nutrient deficiencies, increased cholesterol levels, and negative impacts on heart health. Additionally, the diet may not be sustainable long-term for many individuals, leading to weight regain and emotional eating patterns.
What are the best practices to follow while on a keto diet to minimize risks?
To minimize risks while on a keto diet, focus on consuming whole, unprocessed foods, including plenty of non-starchy vegetables, healthy fats, and high-quality protein sources. Staying hydrated and incorporating physical activity can also support overall health. Monitoring your macronutrient intake and regularly consulting with a healthcare provider can help ensure that you remain healthy while following the diet.
References
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7360072/
- https://www.health.harvard.edu/staying-healthy/the-ketogenic-diet
- Mild and severe acute pancreatitis – Mayo Clinic
- https://www.cdc.gov/healthyweight/healthy_eating/dietary_patterns.html
- https://www.bbc.com/news/health-51064987
- https://www.webmd.com/diet/what-is-the-keto-diet
- https://www.nutrition.gov/topics/whats-new/nutrition-research-keto-diet
- https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/keto-diet-dangerous
- https://www.theguardian.com/society/2020/oct/01/is-the-keto-diet-safe-experts-weigh-in

