The keto diet can indeed be beneficial for cholesterol levels, especially in terms of increasing HDL (good cholesterol) and reducing triglycerides for many individuals. However, it’s essential to recognize that it may also elevate LDL (bad cholesterol) in some cases. This article will explore how the keto diet influences cholesterol levels, the underlying science, and what considerations should be made for individuals monitoring their cardiovascular health.
Understanding Cholesterol: Types and Functions

Cholesterol is a waxy substance found in the cells of the body and in the blood, playing crucial roles in various physiological processes. It is imperative to understand the different types of cholesterol and their functions to grasp how dietary choices affect overall health.
– HDL (High-Density Lipoprotein): Often referred to as “good cholesterol,” HDL helps transport cholesterol away from the arteries and back to the liver, where it is processed and eliminated from the body. Higher levels of HDL are generally associated with a lower risk of heart disease.
– LDL (Low-Density Lipoprotein): Known as “bad cholesterol,” LDL can contribute to the buildup of plaque in the arteries, which can lead to atherosclerosis, heart attack, or stroke if levels are too high. Managing LDL levels is a critical component of cardiovascular health.
– Triglycerides: These are another type of fat found in the blood, and high levels can increase the risk of heart disease. Triglycerides are often associated with obesity, poor diet, and metabolic conditions, making their management important for overall health.
Understanding these types of cholesterol and their functions provides a foundation for evaluating the impact of dietary strategies like the keto diet on cardiovascular health.
How the Keto Diet Works
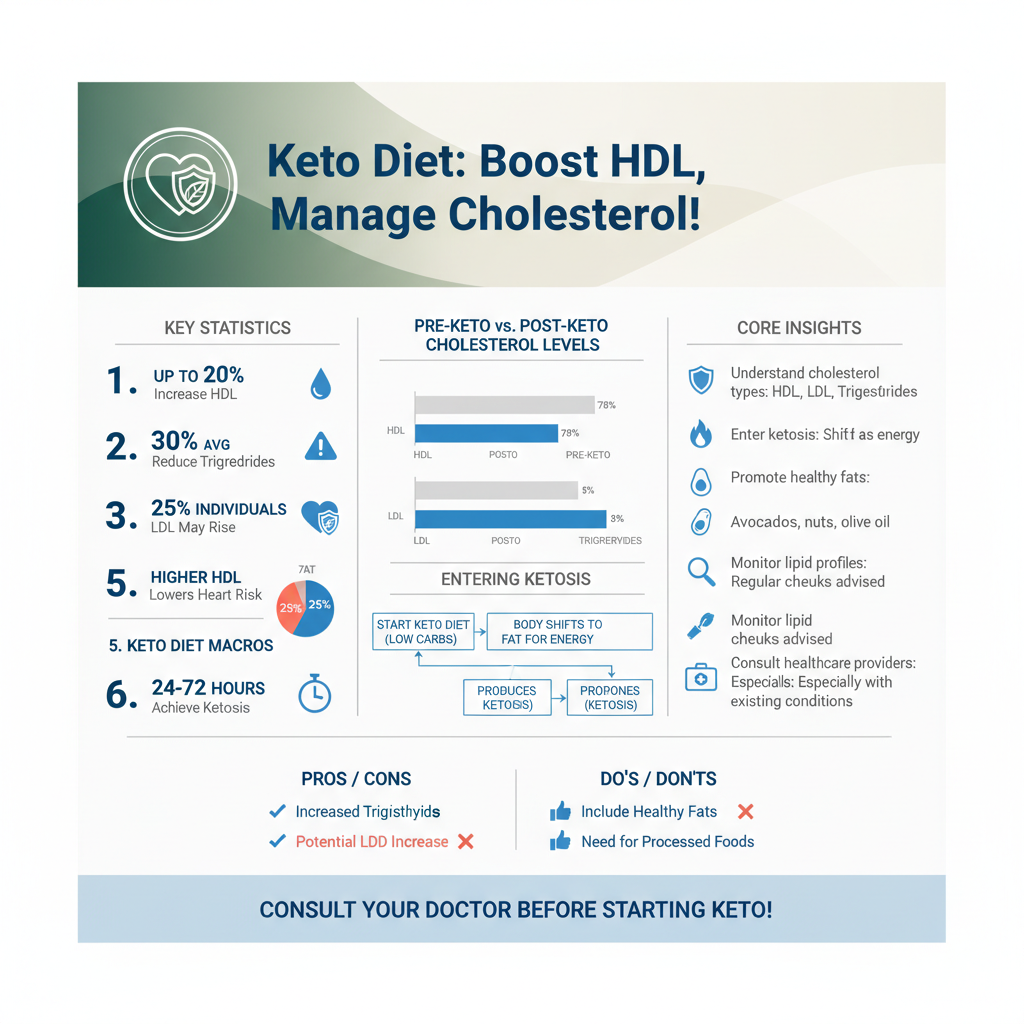

The ketogenic diet is a high-fat, moderate-protein, and very low-carbohydrate eating plan that alters the body’s metabolism. By drastically reducing carbohydrate intake, the body enters a metabolic state known as ketosis, where it relies on fat as its primary energy source instead of carbohydrates.
– Entering Ketosis: When carbohydrate intake is low, insulin levels decrease, and the body begins to break down stored fat into molecules called ketones, which are then used for energy. This shift not only promotes fat loss but also influences the way cholesterol is processed in the body.
– Impact on Metabolism: This metabolic shift can lead to changes in lipid profiles that differ significantly from those seen in standard diets, which are typically higher in carbohydrates and lower in fats. The keto diet encourages the consumption of healthy fats—such as those from avocados, nuts, and olive oil—which can have positive effects on cholesterol levels.
By understanding how the keto diet works at a metabolic level, individuals can better appreciate its potential effects on cholesterol levels and heart health.
Effects of Keto on Cholesterol Levels
Research on the effects of the keto diet on cholesterol levels presents a somewhat mixed picture, which underscores the importance of individual variability.
– Increase in HDL Levels: Many studies have shown that individuals following a ketogenic diet experience a significant increase in HDL cholesterol. This elevation is beneficial as it enhances the body’s ability to remove cholesterol from the bloodstream, thereby potentially reducing heart disease risk.
– LDL Cholesterol Response: Conversely, some individuals may see an increase in LDL cholesterol while on a keto diet. This elevation can be concerning, especially for those already at risk for cardiovascular disease. It is crucial to note that not all LDL particles are equal—some are small and dense, which are more harmful, while others are large and fluffy, which may be less of a concern.
– Reduction in Triglycerides: Most keto dieters report a decrease in triglyceride levels, which is a positive outcome. Lower triglycerides are associated with a reduced risk of heart disease and are often indicative of improved overall metabolic health.
Understanding these effects provides insight into how the keto diet can be tailored to individual health needs and responses.
Individual Variability in Cholesterol Response
The impact of the keto diet on cholesterol levels can vary significantly from person to person due to several factors:
– Genetic Factors: Genetics play a crucial role in how the body metabolizes dietary fats. Some individuals may possess genetic variations that make them more susceptible to increases in LDL cholesterol when consuming a high-fat diet, while others may not experience such changes.
– Pre-existing Conditions: Individuals with existing heart conditions or metabolic disorders may respond differently to the keto diet. It is essential for these individuals to be cautious and consult with healthcare professionals before making significant dietary changes.
– Dietary Composition: The types of fats consumed on a keto diet can also influence cholesterol responses. For instance, incorporating more monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats (found in foods like fatty fish, nuts, and seeds) can promote better lipid profiles than saturated fats (found in certain animal products).
Given this variability, regular monitoring of cholesterol levels is vital for anyone considering or currently following a ketogenic diet.
Recommended Practices for Keto and Heart Health
To maximize the benefits of the keto diet while minimizing potential risks to cholesterol levels, certain practices can be adopted:
– Focus on Healthy Fats: Prioritize sources of healthy fats such as avocados, olive oil, nuts, and fatty fish. These fats can help improve HDL levels and support overall heart health.
– Include Fiber-Rich Foods: While the keto diet is low in carbohydrates, incorporating non-starchy vegetables (such as leafy greens and cruciferous vegetables) can provide essential fiber. Fiber helps regulate cholesterol levels and supports digestive health.
– Consult with a Healthcare Provider: Before initiating the keto diet, particularly for those with pre-existing cholesterol concerns or cardiovascular conditions, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare provider or a registered dietitian. They can help tailor dietary choices to individual health needs and monitor progress effectively.
By adopting these practices, individuals can enhance their experience on the keto diet while prioritizing their heart health.
Monitoring Your Cholesterol on Keto
Monitoring cholesterol levels is crucial for anyone on the keto diet, especially for those concerned about heart health. Here are some actionable insights for effective monitoring:
– Regular Blood Tests: Routine blood tests can help track changes in cholesterol levels over time, providing valuable insights into how the diet is affecting overall lipid profiles. It is advisable to conduct these tests every three to six months, depending on individual risk factors.
– Keeping a Food Diary: Maintaining a food diary can help individuals identify which foods may be influencing their cholesterol levels. By recording meals and symptoms, dieters can make informed adjustments to their dietary choices.
– Adjusting Dietary Choices: Based on cholesterol test outcomes, individuals can modify their dietary strategies. For example, if LDL levels are elevated, they may choose to reduce saturated fat intake while increasing fiber consumption.
By implementing monitoring strategies, individuals can make informed choices and optimize their keto diet for better heart health outcomes.
The keto diet can be beneficial for cholesterol levels, primarily by raising HDL and lowering triglycerides, but it may also increase LDL in some individuals. This duality underscores the importance of personalized approaches to diet and health. Regular monitoring and collaboration with a healthcare professional are crucial for anyone considering this dietary strategy, especially those with pre-existing cardiovascular conditions. Start by assessing your current cholesterol levels and discussing the keto diet with a nutritionist or doctor to tailor it to your individual health needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is the ketogenic diet good for cholesterol levels?
The ketogenic diet can have varying effects on cholesterol levels, depending on individual responses and the types of fats consumed. While some people may experience an increase in LDL cholesterol (often referred to as “bad” cholesterol), others may see improvements in their HDL cholesterol (the “good” cholesterol). It’s important to focus on healthy fats, such as those from avocados, nuts, and olive oil, to promote better heart health while on a keto diet.
How does the keto diet impact triglyceride levels?
The ketogenic diet is often associated with lower triglyceride levels, which can be beneficial for heart health. By significantly reducing carbohydrate intake, the body shifts to burning fat for fuel, which can lead to weight loss and a decrease in triglyceride levels. However, individual results may vary, so it’s crucial to monitor these levels with your healthcare provider when starting the diet.
Why do some people experience a rise in cholesterol while on keto?
Some individuals may see an increase in cholesterol levels while on the ketogenic diet due to increased saturated fat intake and rapid weight loss, which can release stored cholesterol into the bloodstream. Additionally, genetic factors, such as familial hypercholesterolemia, can play a role in how one’s body responds to dietary changes. Regular monitoring and consultation with a healthcare professional can help manage these changes effectively.
What types of fats should I focus on for heart health while following a keto diet?
When following a ketogenic diet, it’s essential to prioritize healthy fats that support heart health. Focus on unsaturated fats from sources like avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil, as well as omega-3 fatty acids from fatty fish like salmon. Limiting saturated fats from processed foods and red meat can help maintain balanced cholesterol levels and support overall cardiovascular health.
Which tests should I get to monitor my cholesterol while on the keto diet?
To effectively monitor your cholesterol levels while on the ketogenic diet, consider getting a lipid panel test, which measures total cholesterol, LDL, HDL, and triglycerides. It’s also worthwhile to discuss with your healthcare provider about advanced lipid testing that can provide more detailed insights into particle size and density, helping to assess your heart health more accurately while on a keto plan.
References
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7078664/
- https://www.health.harvard.edu/staying-healthy/the-truth-about-the-ketogenic-diet
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/nutrition-and-healthy-eating/expert-answers/keto-diet/faq-20407588
- https://www.heart.org/en/healthy-living/healthy-eating/eat-smart/nutrition-basics/what-is-the-ketogenic-diet
- https://www.cdc.gov/heartdisease/healthy_living.htm
- https://www.webmd.com/diet/what-is-the-ketogenic-diet
- https://www.verywellfit.com/the-ketogenic-diet-5119246

