The ketogenic diet can be safe for many diabetics, but it requires careful management and monitoring. By shifting the body’s primary energy source from carbohydrates to fats, the keto diet has the potential to enhance blood sugar control and support weight loss. However, individuals with diabetes should approach this dietary change with caution and consult healthcare professionals to navigate the associated risks effectively.
Understanding the Keto Diet

The ketogenic diet is a high-fat, low-carb eating plan designed to shift the body into a metabolic state known as ketosis, where it burns fat for energy instead of carbohydrates. This dietary approach significantly reduces carbohydrate intake, typically allowing about 20 to 50 grams of carbohydrates per day, while encouraging increased consumption of fats. The macronutrient breakdown for a standard ketogenic diet usually consists of approximately 70% fat, 25% protein, and a mere 5% carbohydrates. This dramatic shift in macronutrient ratios can lead to profound changes in how the body processes energy, offering a unique avenue for management of diabetes.
For diabetics, understanding the mechanics of ketosis is crucial. In this state, the liver converts fatty acids into ketones, which serve as an alternative energy source. This metabolic adaptation can help stabilize blood glucose levels, an essential factor for those managing diabetes.
Benefits of Keto for Diabetics
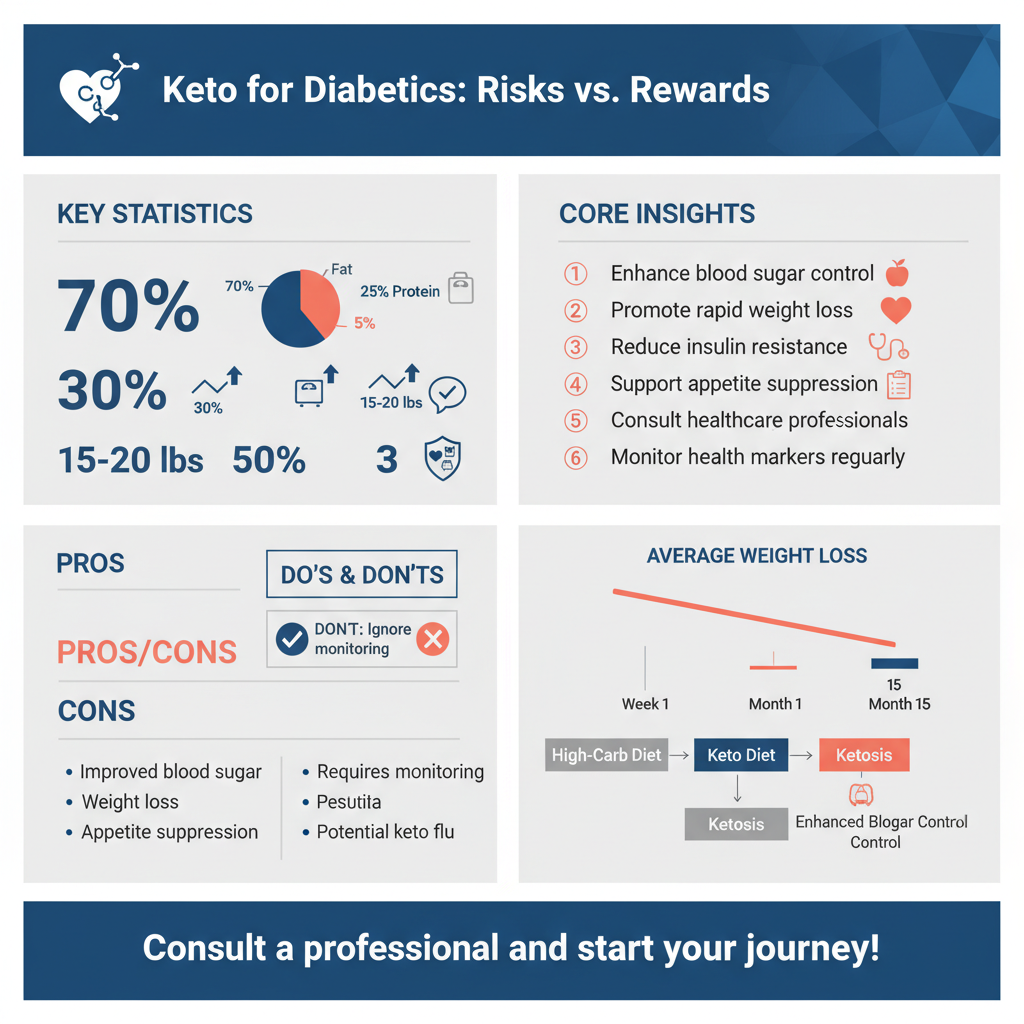

One of the primary benefits of adopting a ketogenic diet for diabetics is improved blood sugar control. Research has indicated that many individuals with diabetes experience better glycemic control and reduced insulin resistance when following a low-carb, high-fat diet. This is particularly beneficial for those with type 2 diabetes, where insulin sensitivity can be significantly enhanced through dietary approaches that limit carbohydrate intake.
Additionally, weight loss is another compelling advantage of the ketogenic diet. Excess weight is a common concern for many diabetics, as it can exacerbate insulin resistance and complicate blood sugar management. The keto diet promotes rapid weight loss by encouraging the body to use stored fat for fuel. In many cases, individuals report losing significant weight in a relatively short period, which can lead to improved health markers, including lower blood pressure and better cholesterol levels.
Moreover, the appetite-suppressing effects of a high-fat diet can help individuals adhere to a caloric deficit, making it easier to achieve and maintain a healthy weight.
Potential Risks of Keto for Diabetics
While there are notable benefits, it is critical to acknowledge the potential risks associated with the ketogenic diet, especially for diabetics. One significant concern is the risk of hypoglycemia, or dangerously low blood sugar levels. Individuals who are on insulin or certain diabetes medications may experience rapid changes in blood sugar due to the drastic reduction in carbohydrate intake. This can lead to confusion, dizziness, or even loss of consciousness if not carefully monitored.
Another risk is the potential for nutrient deficiencies. The restrictive nature of the ketogenic diet can limit the intake of essential nutrients found in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. For instance, many fruits that are high in vitamins and antioxidants are also high in carbohydrates, making them less suitable for a strict ketogenic regime. This can lead to deficiencies in important nutrients, such as fiber, vitamins A and C, and potassium, which are crucial for overall health and wellness.
Furthermore, some individuals may experience side effects commonly referred to as the “keto flu,” which can include fatigue, headache, irritability, and nausea during the initial adaptation phase. While these symptoms are often temporary, they can be challenging for those already managing a chronic condition like diabetes.
Monitoring Your Health on Keto
For individuals with diabetes considering the ketogenic diet, regular monitoring of blood sugar levels is essential. Frequent checks can help prevent complications associated with both hyperglycemia (high blood sugar) and hypoglycemia. It is advisable to keep a log of blood sugar readings to identify patterns and make necessary adjustments to diet or medication.
Additionally, consulting with healthcare professionals is paramount when making any significant dietary changes. A registered dietitian or a doctor familiar with diabetes management can provide personalized guidance tailored to individual health needs. They can help design a meal plan that ensures nutritional adequacy while still promoting ketosis, as well as recommend necessary adjustments in medication to avoid adverse effects on blood sugar levels.
Tips for Starting Keto Safely
Transitioning to a ketogenic diet should be done gradually to allow the body to adjust without experiencing drastic changes. A gradual reduction in carbohydrates over several weeks can minimize the risk of side effects and allow for a smoother adaptation to ketosis.
Focusing on healthy sources of fats is also crucial. Incorporate foods like avocados, nuts, seeds, olive oil, and fatty fish, while avoiding unhealthy trans fats often found in processed foods. Additionally, make sure to maintain hydration and consider electrolyte supplementation, as the initial stages of ketosis can lead to increased water loss and electrolyte imbalances.
It’s also beneficial to prepare meals and snacks in advance to ensure that healthy, keto-friendly options are readily available. This can help prevent the temptation to revert to high-carb foods, especially during busy or stressful times.
Real-Life Success Stories
Many individuals with diabetes have reported positive experiences and lifestyle transformations after adopting the keto diet. Testimonials highlight improved energy levels, better blood sugar control, and significant weight loss. For instance, one individual shared how the keto diet helped lower their A1C, a key marker of long-term blood sugar levels, allowing them to reduce their medication dosage significantly.
Moreover, community support plays a vital role in the success of adopting a ketogenic lifestyle. Many online forums and local groups offer encouragement, recipe sharing, and tips for navigating social situations while adhering to a keto diet. These resources can be invaluable for those looking to stay motivated and informed throughout their journey.
In summary, while the ketogenic diet can be safe and beneficial for many diabetics, it requires careful planning and monitoring. If you’re considering this lifestyle change, consult with a healthcare provider to create a tailored approach that suits your individual health needs. Start your journey to better health today by exploring keto-friendly recipes and connecting with a supportive community.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is the keto diet safe for diabetics?
The keto diet can be safe for many diabetics, particularly those with Type 2 diabetes, as it often helps stabilize blood sugar levels and reduce insulin resistance. However, it’s crucial for individuals with diabetes to consult their healthcare provider before starting a keto diet, as it may require adjustments in medication and careful monitoring of blood sugar levels to avoid hypoglycemia.
How does the keto diet affect blood sugar levels in diabetics?
The keto diet typically lowers blood sugar levels due to its low carbohydrate content, which minimizes the spikes that often occur with higher carb intake. By promoting a state of ketosis, where the body burns fat for fuel instead of glucose, many diabetics experience improved glycemic control. However, it is essential to monitor blood glucose regularly during this dietary change, as individual responses can vary.
What should diabetics consider before starting a keto diet?
Before starting a keto diet, diabetics should consider their current medication regimen, particularly insulin, as lower carbohydrate intake may require dosage adjustments. It’s also important to evaluate personal health goals, any existing medical conditions, and the potential need for ongoing blood sugar monitoring. Collaborating with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian can provide personalized guidance and support.
Which foods are best for diabetics on a keto diet?
Diabetics following a keto diet should focus on whole, nutrient-dense foods that are low in carbs but high in healthy fats and proteins. Ideal food choices include avocados, nuts, seeds, leafy greens, fatty fish, and non-starchy vegetables. Additionally, it’s essential to avoid processed foods, sugars, and high-carb items to maintain stable blood sugar levels.
Why might a diabetic choose the keto diet over other diets?
A diabetic might choose the keto diet over other diets because it can effectively help with weight loss, improve insulin sensitivity, and lower blood sugar levels. The high-fat, low-carb approach can lead to reduced cravings and more stable energy levels throughout the day. However, it’s important to note that dietary preferences and individual health goals should guide this choice, so personalized advice is recommended.
References
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7070840/
- https://www.diabetes.org/healthy-living/recipes-nutrition/understanding-carb-counting
- https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/managing/eating.html
- https://www.webmd.com/diet/what-is-the-keto-diet
- https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/keto-diet-and-diabetes
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/nutrition-and-healthy-eating/expert-answers/keto-diet-and-diabetes/faq-20426726


