The keto diet can have mixed effects on heart health. While it may benefit some individuals by aiding weight loss and improving certain metabolic markers, it can also raise cholesterol levels in others. This article will explore the potential risks and benefits of a ketogenic diet in relation to heart health so that you can make an informed decision.
Understanding the Keto Diet

The ketogenic diet is a high-fat, low-carbohydrate eating plan that shifts the body into a state of ketosis. In this metabolic state, the body becomes more efficient at burning fat for energy instead of relying on carbohydrates. The typical macronutrient breakdown for the keto diet involves reducing carbohydrate intake to about 5-10% of total daily calories while increasing fat intake to around 70-80%. This drastic reduction in carbs forces the body to produce ketones from fat in the liver, which serve as an alternative energy source. While many individuals report benefits such as weight loss and increased energy, understanding the diet’s impact on heart health is crucial for making informed dietary choices.
Potential Benefits of Keto for Heart Health
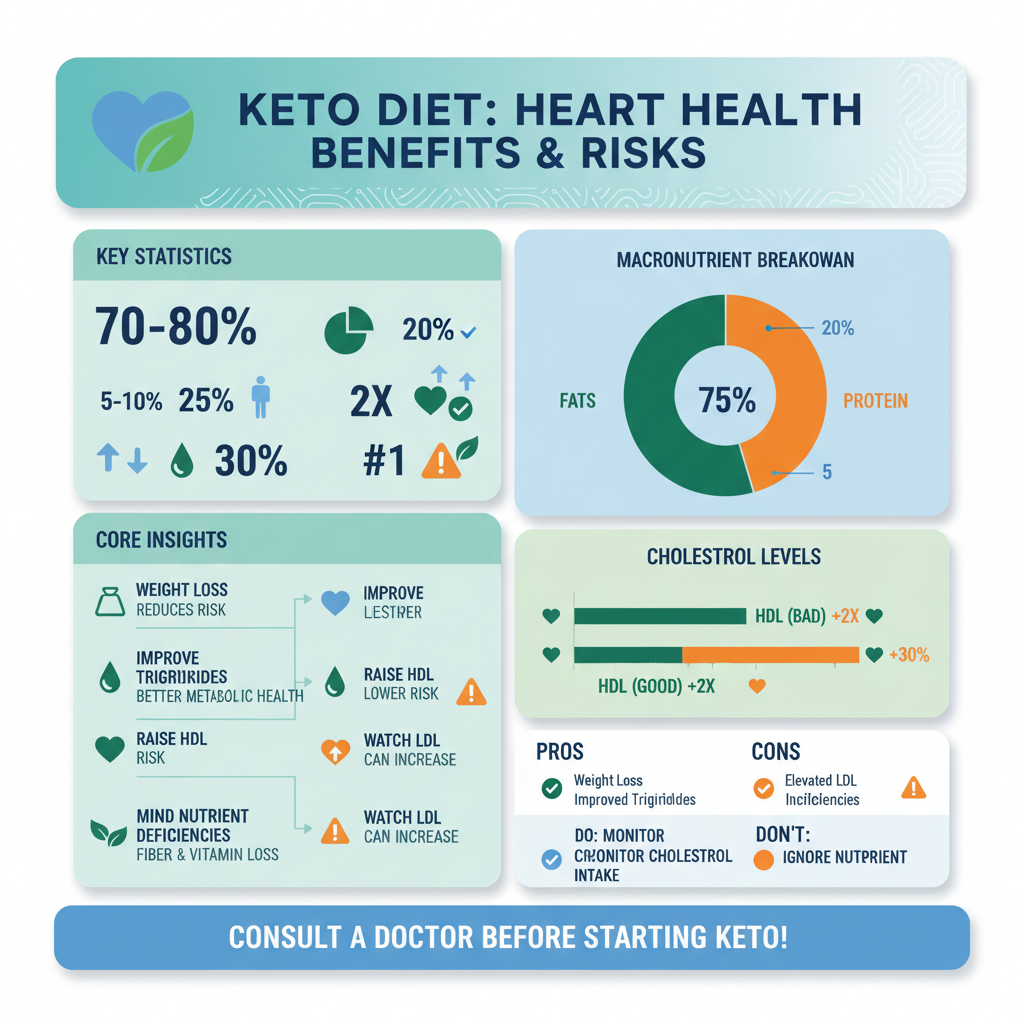

Some studies suggest that the keto diet can lead to significant weight loss, which may reduce the risk of heart disease. Excess weight is a known risk factor for various cardiovascular issues, including hypertension and dyslipidemia. By promoting fat loss, particularly in the abdominal area, the keto diet may help in lowering these risks.
Additionally, the ketogenic lifestyle has been shown to improve triglyceride levels and raise HDL (high-density lipoprotein) cholesterol, commonly referred to as “good cholesterol.” Higher HDL levels are associated with a reduced risk of heart disease, while lower triglyceride levels can indicate improved metabolic health. For instance, a study in the journal Nutrition & Metabolism indicated that participants on a ketogenic diet experienced significant improvements in their lipid profiles, suggesting potential heart health benefits.
Risks Associated with Keto and Heart Health
Despite its potential benefits, the keto diet can increase LDL (low-density lipoprotein) levels, often referred to as “bad cholesterol,” in some individuals. Elevated LDL levels are associated with a higher risk of heart disease, particularly when they become oxidized. The diet’s high saturated fat content, common in many keto meal plans, can further exacerbate this issue, leading to concerns among healthcare professionals.
Moreover, the restrictive nature of the keto diet may lead to nutrient deficiencies, particularly in fiber and essential vitamins found in fruits and whole grains. These deficiencies can have downstream effects on cardiovascular health, as fiber is known to play a role in reducing cholesterol levels and maintaining a healthy heart.
Key Nutrients for Heart Health on Keto
When following a ketogenic diet, it is essential to focus on incorporating healthy fats rather than relying solely on saturated fats. Sources of healthy fats include avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil, all of which can contribute positively to heart health. For example, olive oil is rich in monounsaturated fats, which have been linked to reduced inflammation and improved cholesterol levels.
Incorporating fiber-rich vegetables into the diet is also crucial. Low-carb vegetables, such as leafy greens, broccoli, and cauliflower, can provide essential nutrients and fiber while keeping carbohydrate intake within keto limits. Balancing the diet with these nutrient-dense foods can help mitigate some of the risks associated with the keto diet and support overall heart health.
Individual Responses to the Keto Diet
It’s important to recognize that heart health can vary widely among individuals on the keto diet due to factors such as genetics, lifestyle, and pre-existing conditions. For instance, some individuals may experience improved cardiovascular markers, while others may see increased cholesterol levels. Regular monitoring of cholesterol levels and other heart health indicators is essential for those on the diet, especially if they have a history of heart disease or other risk factors.
Individual responses can also be influenced by the specific types of fats consumed. For example, individuals who emphasize unsaturated fats may experience more favorable heart health outcomes compared to those who consume higher amounts of saturated fats. Thus, personalizing the approach to the keto diet based on individual health profiles can be crucial.
Expert Opinions on Keto and Heart Health
Cardiology experts often recommend a balanced approach to dietary changes, emphasizing whole foods over processed options. Many professionals advocate for a diet that includes a variety of food groups to ensure adequate nutrient intake while still promoting heart health. Consulting with a healthcare provider before starting the keto diet is highly advisable, as they can help tailor the diet to individual health needs and monitor any potential risks.
In recent years, some experts have called for a reevaluation of the traditional low-fat versus high-fat debate, suggesting that the focus should be on the quality of fats consumed rather than merely the quantity. This perspective acknowledges the potential for healthy fats to support heart health when integrated thoughtfully into the diet.
Making Informed Choices
When considering the keto diet, it is important to evaluate personal health goals and family history. If weight loss or improved metabolic markers are the primary objectives, the keto diet may provide benefits. However, if there is a family history of heart disease or pre-existing conditions, it may be prudent to explore alternative diets that offer similar benefits without the potential heart risks associated with a high-fat, low-carb approach.
Many individuals may find success with Mediterranean or plant-based diets, which emphasize whole foods, healthy fats, and plenty of fruits and vegetables. These diets are often associated with lower cardiovascular risk and can be more sustainable in the long term.
Making an informed decision about the keto diet and its impact on heart health is crucial. While it can offer benefits, particularly in weight management, it may pose risks for some individuals. Always consult with a healthcare professional before making significant dietary changes, and monitor your health closely to ensure the best outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is a keto diet bad for your heart health?
The keto diet, which is high in fats and low in carbohydrates, can have mixed effects on heart health. Some studies suggest that it may raise levels of LDL cholesterol, often referred to as “bad” cholesterol, which could increase the risk of heart disease. However, other research indicates that the diet can improve certain risk factors, such as body weight and blood sugar levels. It’s essential to focus on the types of fats consumed—prioritizing healthy fats like avocados and nuts over saturated fats—when following a keto diet for optimal heart health.
How does the keto diet affect cholesterol levels?
The keto diet can significantly influence cholesterol levels due to its high-fat content. While some individuals experience an increase in LDL cholesterol, others may see improvements in their HDL cholesterol, known as “good” cholesterol. Monitoring your lipid profile regularly is crucial, as individual responses can vary. Including healthy fats, such as olive oil and fatty fish, may help mitigate potential negative effects on cholesterol while following a keto diet.
Why might a keto diet be considered risky for some individuals?
A keto diet may pose risks for certain individuals, particularly those with pre-existing heart conditions, high cholesterol, or metabolic disorders. The drastic reduction in carbohydrates can lead to nutritional deficiencies and may exacerbate existing health issues. Additionally, the high intake of saturated fats might not be suitable for everyone, especially those predisposed to cardiovascular diseases. Consulting with a healthcare provider before starting a keto diet is crucial for assessing individual risks and benefits.
What are the best fats to consume on a keto diet for heart health?
To promote heart health while on a keto diet, it’s vital to focus on consuming healthy fats. The best options include monounsaturated fats, such as those found in olive oil, avocados, and nuts, as well as omega-3 fatty acids found in fatty fish like salmon and mackerel. These fats can support cardiovascular health and help maintain healthy cholesterol levels. Limiting saturated fats from processed meats and full-fat dairy and avoiding trans fats found in many processed foods is equally important.
Which foods should be avoided on a keto diet to protect heart health?
To protect heart health while following a keto diet, it’s important to avoid certain foods high in unhealthy fats. Processed meats, fried foods, and full-fat dairy products can be high in saturated and trans fats, which may negatively impact cholesterol levels. Additionally, sugary foods and refined carbohydrates should be limited, as they can contribute to inflammation and other heart disease risk factors. Instead, prioritize whole, nutrient-dense foods that provide healthy fats and essential nutrients.
References
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7071239/
- https://www.health.harvard.edu/staying-healthy/the-ketogenic-diet
- Not Found | American Heart Association | American Heart Association
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/nutrition-and-healthy-eating/expert-answers/keto-diet/faq-20458666
- https://www.jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/2766409
- https://www.cdc.gov/heartdisease/healthy_lifestyle.htm
- https://www.webmd.com/diet/what-is-the-keto-diet#1


