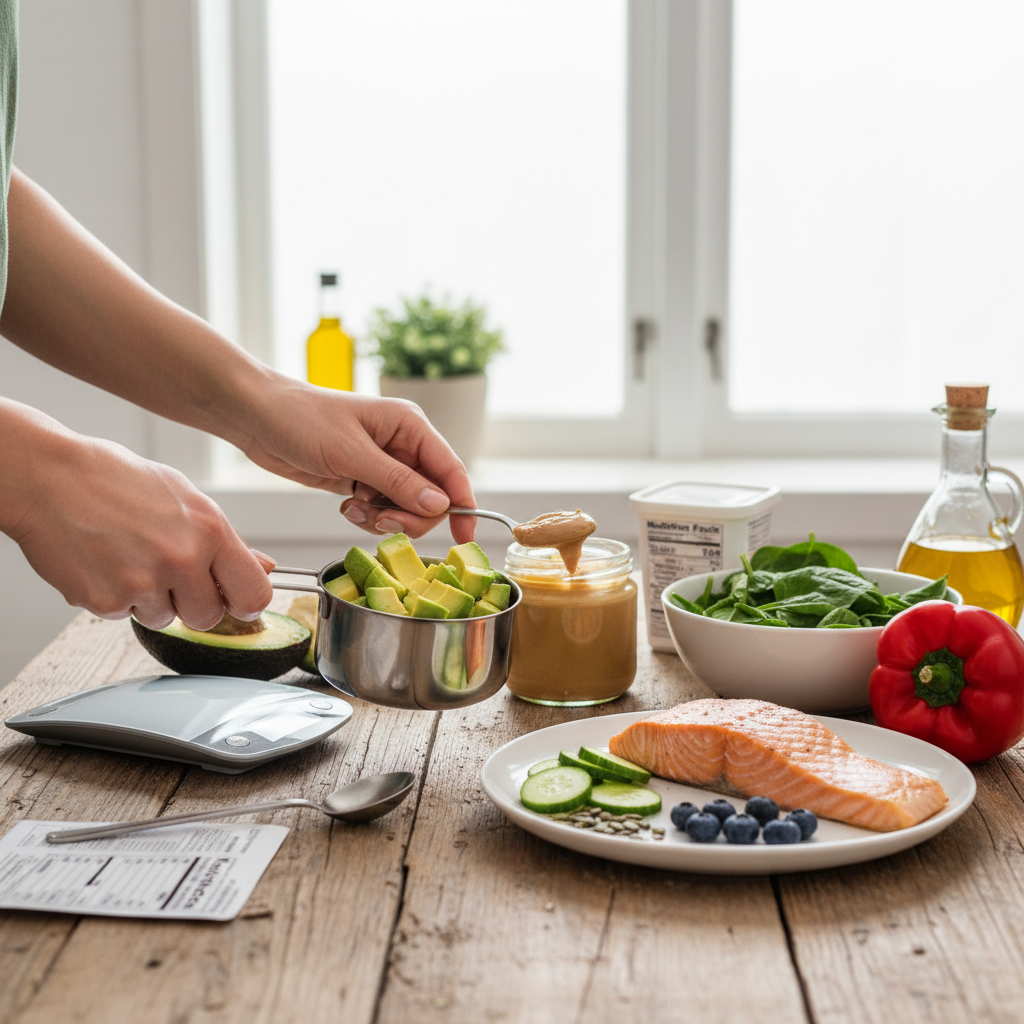
The ideal fat intake on a keto diet typically ranges from 70% to 80% of your total daily calories. This high-fat consumption is essential for achieving and maintaining ketosis, where your body burns fat for fuel instead of carbohydrates. By prioritizing the right types of fats and calculating your daily needs, you can effectively navigate your keto journey. In this article, you’ll learn how to calculate your fat needs, the types of fats to prioritize, and tips for balancing your macronutrients effectively.
Understanding Macronutrient Ratios

The standard keto ratio: At its core, a ketogenic diet is characterized by a specific macronutrient ratio that promotes fat burning. Generally, the standard breakdown consists of about 70-80% of total calories coming from fats, 15-25% from protein, and 5-10% from carbohydrates. This balanced approach ensures that the body enters a state of ketosis, where it begins to utilize fat as its primary energy source.
Importance of ratios: Understanding these ratios is crucial for anyone embarking on a keto diet, as they directly influence your metabolic processes. When carbohydrate intake is significantly reduced, the body is forced to turn to fat for energy, which promotes weight loss and improves metabolic health. Adhering strictly to these macronutrient ratios not only supports weight loss but can also enhance mental clarity and energy levels.
Calculating Your Daily Fat Intake
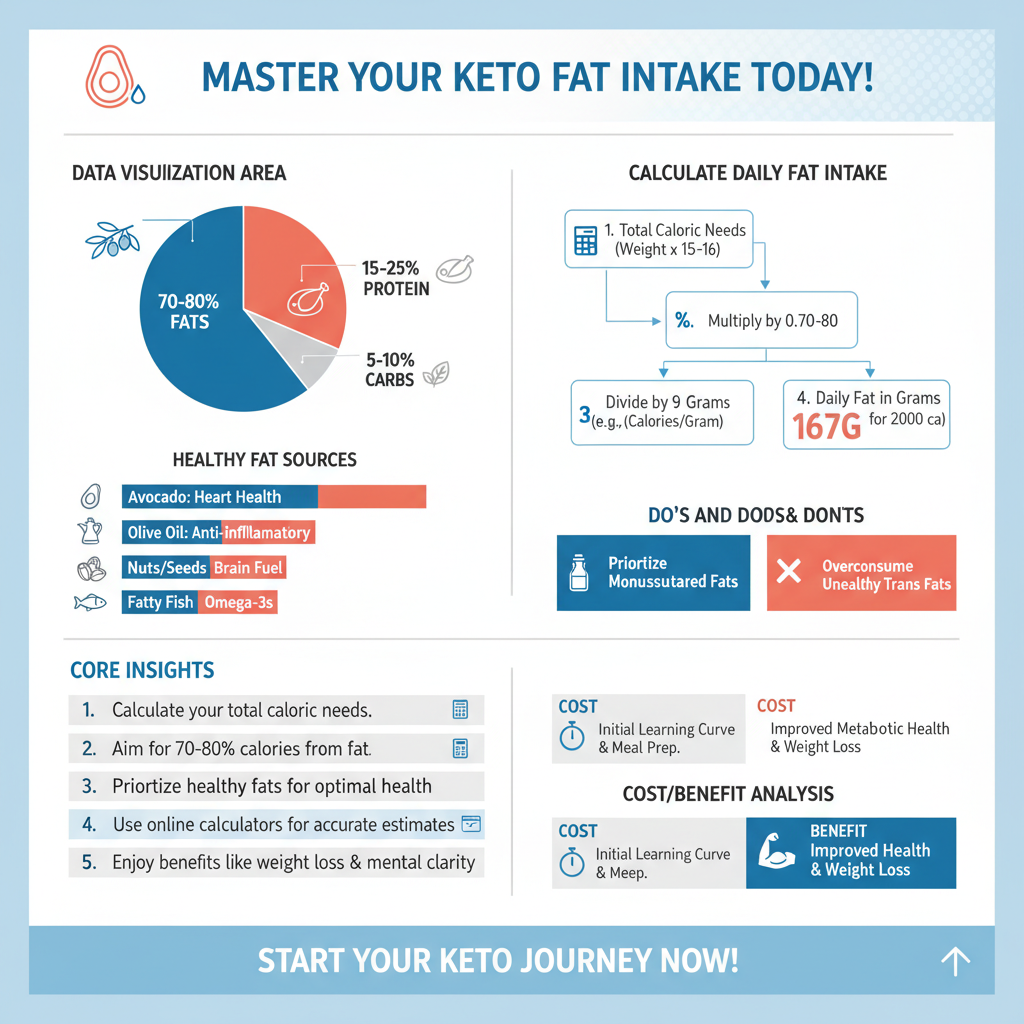

Total daily caloric needs: To determine how much fat you should consume daily, start by calculating your total caloric needs. This calculation can vary based on factors such as age, gender, weight, height, and activity level. Numerous online calculators can assist in estimating your daily caloric needs, but a simple formula is to multiply your weight in pounds by 15-16 for a rough estimate of your maintenance calories.
Fat grams calculation: Once you have your total caloric needs, you can calculate your desired fat intake. For example, if your daily caloric requirement is 2,000 calories and you aim for 75% fat, you would multiply 2,000 by 0.75 to get 1,500 calories from fat. Since each gram of fat provides approximately 9 calories, you would then divide 1,500 by 9, resulting in about 167 grams of fat per day. This calculation provides a clear target for your daily fat consumption.
Types of Fats to Focus On
Healthy fats: Not all fats are created equal, and it’s essential to prioritize healthy fats for optimal health. Sources of monounsaturated fats, such as avocados, olive oil, and nuts, are excellent choices as they support heart health and reduce inflammation. Polyunsaturated fats, found in fatty fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts, are also beneficial due to their Omega-3 content, which is crucial for brain health and overall wellness.Saturated fats: While saturated fats have historically been portrayed negatively, they play a significant role in a keto diet. Sources like coconut oil, grass-fed butter, and full-fat dairy can provide essential nutrients and energy while promoting ketosis. Recent studies suggest that moderate consumption of saturated fats may not have the adverse effects previously thought, especially when derived from whole food sources. However, it remains important to consume these fats in moderation and to balance them with unsaturated fats for overall health.
Common Mistakes in Fat Consumption
Overconsumption: A common pitfall in a keto diet is the overconsumption of unhealthy fats. Many individuals mistakenly believe that any fat is good fat; however, indulging in processed fats or trans fats can lead to detrimental health effects. It’s crucial to focus on whole, unprocessed sources of fat to enhance your health while maintaining ketosis.
Underestimating portion sizes: Accurately measuring fat portions can significantly impact your dietary goals. Many people underestimate the amount of fat they consume, leading to unintentional overconsumption or underconsumption. Utilizing kitchen scales, measuring cups, and food tracking apps can help ensure that you are adhering to your fat intake goals while providing clarity on portion sizes.
Adjusting Fat Intake for Individual Needs
Personalizing your diet: The keto diet is not a one-size-fits-all approach. It’s essential to personalize your fat intake based on individual factors such as weight loss goals, activity levels, and specific health conditions. For instance, someone engaged in high-intensity workouts may require a slightly higher fat intake to support energy levels, whereas someone with a sedentary lifestyle may need less. Regularly re-evaluating your goals and adjusting your fat intake accordingly can enhance your success on the diet.
Monitoring ketone levels: Keeping track of your ketone levels can serve as a valuable indicator of whether you are successfully maintaining ketosis. There are several methods to test ketones, including urine strips, blood monitors, or breath analyzers. Regular monitoring allows you to make informed adjustments to your fat intake and overall macronutrient ratios, ensuring that you remain in a state of ketosis.
Meal Planning for a High-Fat Diet
Sample meal ideas: Crafting meals that align with a high-fat intake can be both enjoyable and nutritious. Breakfast could include scrambled eggs cooked in coconut oil with avocado on the side. For lunch, consider a salad topped with grilled chicken, olive oil, and crushed nuts. Dinner might feature a fatty fish, such as salmon, paired with sautéed greens cooked in butter.
Staying Motivated on Your Keto Journey
Setting realistic goals: Staying motivated on a keto diet requires setting achievable milestones. Instead of focusing solely on weight loss, consider setting performance goals, such as running a certain distance or lifting a specific weight. Celebrating small victories can keep you engaged and motivated throughout your journey.
Community support: Engaging with a supportive community can provide encouragement and valuable insights as you navigate your keto lifestyle. Whether through online forums, social media groups, or local meet-ups, connecting with others who share similar goals can offer motivation, recipe ideas, and emotional support during challenging times.
By focusing on the right amount of fat and the types of fats included in your diet, you can successfully navigate the keto lifestyle. Remember to regularly evaluate your progress and adjust your intake as necessary to ensure you remain in ketosis and continue to meet your wellness goals. For more tips and recipes, subscribe to our newsletter or explore our keto resources!
Frequently Asked Questions
How much fat should I consume on a keto diet?
On a ketogenic diet, fat typically makes up about 70-80% of your total daily caloric intake. For most people, this translates to approximately 150-200 grams of fat per day, depending on individual calorie needs and weight loss goals. It’s essential to focus on healthy fats, such as avocados, olive oil, and fatty fish, while limiting processed fats that can be detrimental to health.
Why is fat intake so high on a keto diet?
The primary goal of the keto diet is to enter a state of ketosis, where the body burns fat for fuel instead of carbohydrates. A high fat intake is crucial because it provides the necessary energy that the body needs while keeping carbohydrate consumption low. This high-fat approach helps to suppress hunger, stabilize blood sugar levels, and promote fat loss, making it effective for weight management.
What types of fats are best for a keto diet?
The best types of fats for a keto diet include monounsaturated fats like olive oil and avocados, saturated fats from sources like grass-fed butter and coconut oil, and omega-3 fatty acids found in fatty fish and flaxseeds. It’s important to avoid trans fats and highly processed oils, as these can lead to inflammation and other health issues. Incorporating a variety of healthy fats can help ensure you are getting a balanced nutrient profile.
How can I track my fat intake on a keto diet?
Tracking fat intake on a keto diet can be effectively done using mobile apps like MyFitnessPal or Cronometer, which allow you to log your food and monitor macronutrient ratios. Additionally, weighing and measuring your food can provide a more accurate assessment of your fat consumption. By paying attention to portion sizes and reading nutrition labels, you can ensure that you stay within your desired fat intake range.
Which foods should I avoid to maintain my fat intake on a keto diet?
To maintain your fat intake on a keto diet, you should avoid high-carb foods such as bread, pasta, rice, sugary snacks, and most fruits. Additionally, limit processed foods that are high in unhealthy fats, like fried foods and packaged snacks. Instead, focus on whole, nutrient-dense foods that provide healthy fats and keep your carbohydrate intake low to effectively promote ketosis.
References
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6073830/
- The Ketogenic Diet: A Detailed Beginner’s Guide to Keto
- https://www.webmd.com/diet/what-is-the-ketogenic-diet
- https://www.diabetes.org/nutrition/healthy-foods/ketogenic-diet
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6831178/
- https://www.eatright.org/health/dietary-guidelines-and-myplate/understanding-the-ketogenic-diet
- https://www.cdc.gov/healthyweight/assessing/bmi/adult_bmi/english_bmi_calculator/bmi_calculator.html


