The ketogenic diet typically limits carbohydrate intake to about 20 to 50 grams per day, depending on individual factors and goals. This low-carb approach is designed to shift the body into a state of ketosis, where it burns fat for fuel instead of carbohydrates. By understanding these carb limits, as well as how to effectively manage and track your intake, you can successfully navigate the complexities of a keto lifestyle. In this article, we will explore the specifics of carb limits in a keto diet, potential variations, and practical tips for maintaining your carb intake.
Understanding the Ketogenic Diet

The primary goal of a keto diet is to enter ketosis by drastically reducing carbohydrate intake. During ketosis, the body transitions from relying on glucose derived from carbohydrates to using ketones, which are produced from fat breakdown. This metabolic shift can lead to significant weight loss and various health benefits, such as improved mental clarity and reduced hunger. Most ketogenic diets suggest a macronutrient breakdown of approximately 70% fats, 25% protein, and 5% carbs. This high-fat, low-carb ratio is crucial for achieving and maintaining ketosis. Foods that are staples in a keto diet include avocados, nuts, seeds, fatty fish, and low-carb vegetables, while grains, sugars, and many fruits are typically avoided.
Recommended Carb Intake
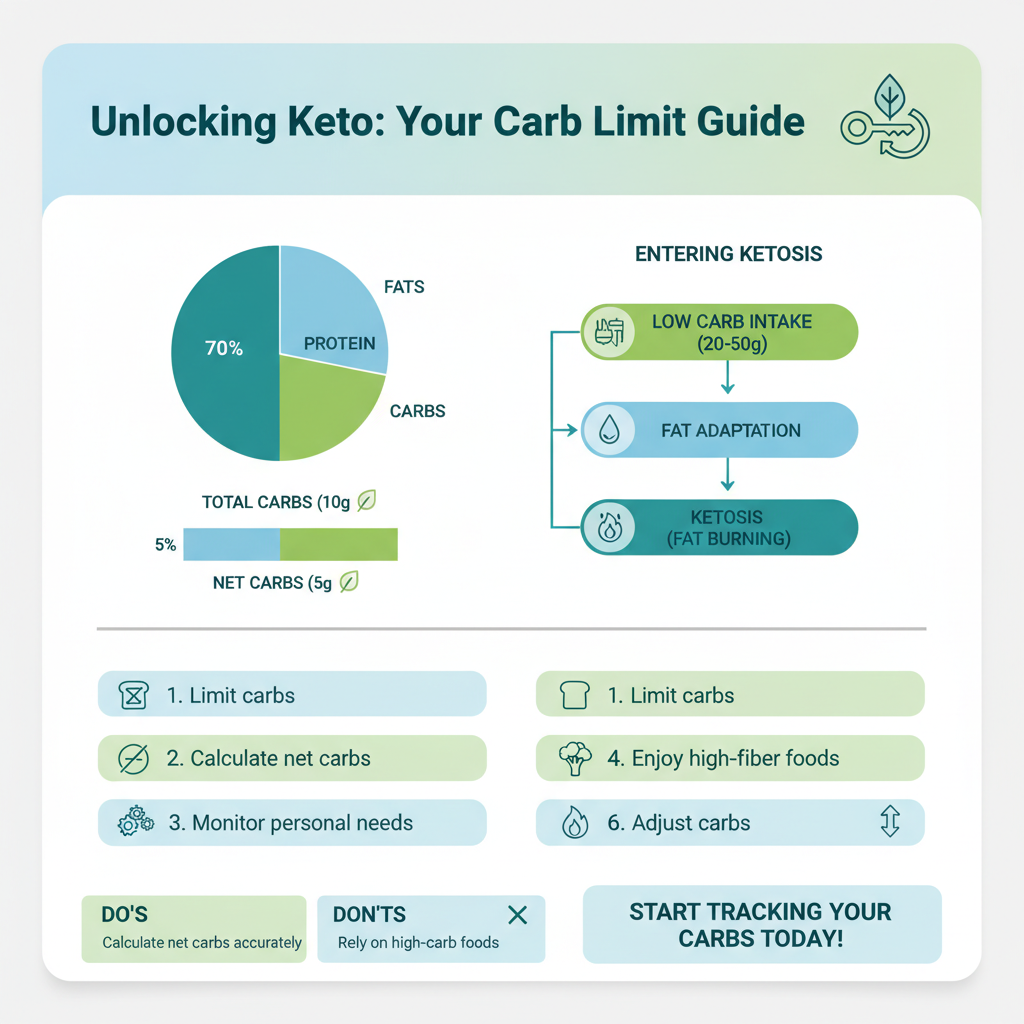

General recommendations suggest staying under 20-50 grams of net carbs per day for most individuals on a ketogenic diet. Net carbs are calculated by subtracting fiber and certain sugar alcohols from total carbohydrates, as these components do not significantly affect blood sugar levels. For example, if a food has 10 grams of total carbohydrates and 5 grams of fiber, the net carb count would be 5 grams. This approach allows individuals to enjoy high-fiber foods that can aid digestion and promote a feeling of fullness without compromising their carb limits. It’s important to note that individual needs may vary, and some might thrive on a slightly higher carb allowance, particularly if they are more active or have a higher metabolic rate.
Factors Influencing Carb Limit
Individual metabolism and activity level can significantly influence how many carbs one can consume while remaining in ketosis. For example, athletes or those engaged in high-intensity training may find they can incorporate a few more carbohydrates without affecting their ketotic state. Additionally, health conditions such as diabetes may require more stringent carbohydrate monitoring. Individuals with insulin resistance or type 2 diabetes may benefit from a stricter carb limit to manage blood sugar levels effectively. Furthermore, age, gender, hormonal changes, and other personal health profiles can also play a role in determining one’s optimal carb intake on a keto diet.
Types of Carbohydrates to Avoid
To maintain an effective ketogenic diet, it’s essential to minimize or eliminate processed foods, sugary snacks, and grains from your meals. These items are often high in carbohydrates and can quickly push you over your daily limit. High-carb vegetables, such as potatoes, corn, and peas, should also be avoided, as they can add up in carb content without providing significant nutritional value. On the other hand, low-carb vegetables like leafy greens, broccoli, and zucchini are excellent substitutes, providing essential vitamins and minerals while keeping your carb intake in check. Fruits should be consumed in moderation; berries, for example, are lower in sugar compared to other fruits and can be enjoyed in small portions.
Tracking Carbohydrates on a Keto Diet
Utilizing apps or food diaries can help track daily carbohydrate intake effectively. Popular keto tracking apps such as MyFitnessPal, Carb Manager, or Cronometer allow users to log their meals and monitor their macronutrient ratios in real-time. Understanding food labels and serving sizes is crucial for accurate carb counting. Many processed foods can contain hidden sugars or carbs, so it’s essential to read labels carefully. For instance, a serving of nut butter may seem low in carbs, but added sugars can elevate the total carb count significantly. Keeping a food diary not only helps in tracking carb intake but can also enhance mindfulness around food choices.
Tips for Staying Within Carb Limits
Meal prepping can help ensure that you stick to your carb limits and avoid impulse eating. By planning your meals ahead of time, you can create balanced dishes that satisfy your hunger while adhering to your dietary restrictions. Incorporating low-carb snacks such as cheese, hard-boiled eggs, or nuts can help maintain energy levels without exceeding your carb limits. Additionally, consider making use of keto-friendly recipes that substitute high-carb ingredients for low-carb alternatives. For example, cauliflower can be used as a rice substitute, or zucchini can be spiralized to create a pasta alternative. These strategies can make it easier to enjoy satisfying meals while staying within your desired carb range.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Many people underestimate the carb content in certain foods, leading to unintentional overconsumption. For instance, condiments like ketchup, sauces, or dressings can contain hidden sugars that add significant carbs to your meal. Not considering hidden carbs in these products can derail your efforts to maintain ketosis. Additionally, relying too heavily on packaged “keto-friendly” snacks can lead to a false sense of security, as some may still contain more carbs than expected. Always check the nutritional information and be vigilant about serving sizes to avoid exceeding your limits.
Maintaining a keto diet requires careful management of carbohydrate intake, typically between 20 and 50 grams daily. By understanding the types of carbs to avoid, tracking your intake, and being aware of personal factors that influence your diet, you can effectively stay in ketosis. If you’re considering starting a keto diet or want to refine your approach, take the time to educate yourself on carb counting and meal planning for better results. With diligence and the right strategies, a ketogenic lifestyle can be both rewarding and sustainable.
Frequently Asked Questions
How many grams of carbs should I consume on a keto diet?
On a standard ketogenic diet, it is generally recommended to limit your carbohydrate intake to about 20 to 50 grams of net carbs per day. This low-carb intake helps your body enter a state of ketosis, where it burns fat for fuel instead of carbohydrates. The exact number can vary based on individual factors such as age, activity level, and weight loss goals, so it’s important to monitor your response and adjust accordingly.
Why is it important to limit carbs on a keto diet?
Limiting carbohydrates is crucial on a keto diet because this restriction is what triggers the metabolic state of ketosis. In ketosis, your body shifts from using glucose as its primary energy source to burning fat for fuel, which can lead to effective weight loss and improved energy levels. High carb intake can hinder this process, preventing you from reaching or maintaining ketosis and thus reducing the diet’s effectiveness.
What are some low-carb foods to include in a keto diet?
When following a keto diet, consider incorporating foods that are low in carbohydrates but high in healthy fats and proteins. Some excellent options include avocados, leafy greens, nuts and seeds, fatty fish, eggs, and full-fat dairy products. These foods can help you stay within your carb limits while providing essential nutrients and promoting satiety.
How can I track my carb intake on a keto diet?
Tracking your carb intake on a keto diet can be done using various methods, including smartphone apps like MyFitnessPal or Cronometer, which allow you to log your food and automatically calculate your daily carb consumption. You can also keep a food diary to manually record your meals and their carb contents, ensuring you remain within your desired range. Regularly checking nutrition labels and using a food scale can further enhance accuracy.
Which types of carbs should I avoid on a keto diet?
On a keto diet, it’s best to avoid high-carb foods such as grains (like bread, pasta, and rice), sugary foods (including candy, desserts, and soft drinks), and starchy vegetables (like potatoes and corn). Additionally, many fruits are high in sugars and should be consumed sparingly. Instead, focus on low-carb vegetables and healthy fats to stay within your carb limits while enjoying a variety of foods.
References
- Ketogenic diet
- The Ketogenic Diet: A Detailed Beginner’s Guide to Keto
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6831285/
- https://www.cdc.gov/healthyweight/assessing/bmi/adult_bmi/index.html
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/nutrition-and-healthy-eating/in-depth/keto-diet/art-20459912
- https://www.webmd.com/diet/what-is-the-keto-diet
- https://www.nutrition.gov/topics/nutrition-101/what-ketogenic-diet

