The ketogenic diet isn’t likely to cause diabetes; in fact, it may improve blood sugar control and insulin sensitivity. However, if you have diabetes or take glucose-lowering medications, the rapid change in your diet can lead to unpredictable blood sugar levels and potential hypoglycemia. It’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider before starting keto to manage these risks effectively. Understanding both benefits and concerns can help you make informed choices about your health journey.
Understanding the Ketogenic Diet
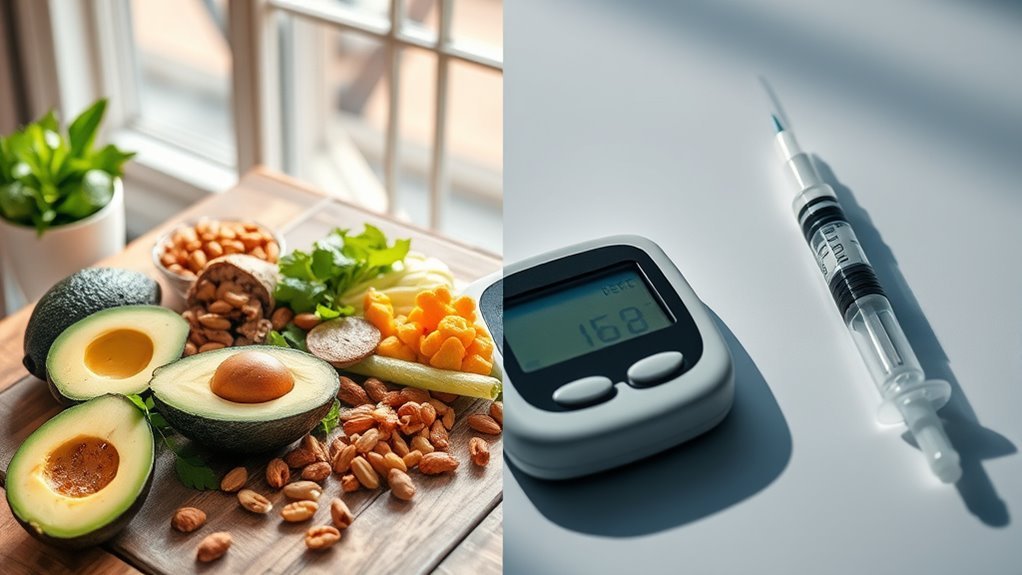
When you explore the ketogenic diet, you’ll find it’s a high-fat, low-carbohydrate eating plan designed to shift your body’s metabolism from burning carbohydrates to fat for fuel. The ketogenic principles emphasize a macro balance, where approximately 70-75% of your daily calories come from fats, 20-25% from proteins, and only about 5-10% from carbohydrates. This shift encourages your body to enter a state of ketosis, where it efficiently uses fat stores for energy. By focusing on healthy fats—like avocados, nuts, and olive oil—you can satisfy hunger while reducing insulin spikes. This approach may offer freedom from constant hunger and energy crashes, allowing you to pursue a lifestyle that aligns with your personal health goals. Understanding these fundamentals can empower your dietary choices.
How Keto Affects Blood Sugar Levels

While the ketogenic diet primarily focuses on reducing carbohydrate intake, its impact on blood sugar levels is significant. By minimizing carbs, your body enters a state of ketosis, where it primarily burns fat for fuel instead of glucose. This shift can lead to more stable blood sugar levels, aiding in blood sugar management and enhancing glucose regulation. For many, this means less fluctuation in insulin levels, which can be beneficial for those concerned about diabetes. However, it’s important to monitor how your body responds, as individual experiences may vary. Ultimately, keto can offer a sense of freedom from constant cravings and energy dips, but understanding its effects on your blood sugar is essential for making informed dietary choices.
Potential Risks for Diabetics

Although the ketogenic diet can offer benefits for blood sugar management, it also poses potential risks for individuals with diabetes. One major concern is the risk of hypoglycemia, especially if you’re on insulin or other glucose-lowering medications. Rapid shifts in your diet can lead to unpredictable blood sugar levels, triggering diabetic complications. Additionally, the high-fat content of keto might raise concerns about heart health, particularly if you’re not monitoring your cholesterol levels. It’s important to consult with your healthcare provider before starting this diet, ensuring it aligns with your individual health needs. Balancing freedom in dietary choices with awareness of these keto risks can help you make informed decisions while managing diabetes effectively.
The Role of Insulin in a Keto Diet
Understanding the role of insulin in a keto diet is vital for those managing diabetes. A keto diet can improve insulin sensitivity, which helps your body utilize glucose more effectively. By considerably reducing carbohydrate intake, you lower insulin levels, which can promote hormonal balance. This shift encourages your body to burn fat for fuel instead of relying on sugar, potentially leading to better blood sugar control. However, it’s important to monitor your insulin levels and consult with a healthcare professional, especially if you’re taking insulin or other diabetes medications. Finding the right balance can empower you to embrace the keto lifestyle while effectively managing your health and achieving greater freedom in your dietary choices.
Long-Term Effects of Ketosis on Metabolism
After exploring how insulin functions within a keto diet, it’s important to look at the long-term effects of ketosis on metabolism. Prolonged ketosis duration can lead to various metabolic adaptations that may impact your overall health.
- Enhanced fat oxidation, allowing your body to efficiently use fat for energy.
- Potential decrease in metabolic rate, which could affect weight management.
- Changes in hormone levels that may influence appetite and energy balance.
While many experience benefits from sustained ketosis, it’s essential to monitor your body’s responses. Each individual’s reaction can vary, meaning what works for you might not be suitable for someone else. Balancing your approach can help you maintain metabolic health while enjoying the freedom a keto lifestyle offers.
1. Can the ketogenic diet cause diabetes?
The ketogenic diet itself does not cause diabetes; in fact, it may help some individuals manage their blood sugar levels. However, the diet is high in fats and low in carbohydrates, which can lead to insulin resistance in some people, particularly if they consume unhealthy fats or do not monitor their macronutrient intake properly. It’s essential for anyone considering keto, especially those with a history of diabetes, to consult a healthcare professional.
2. How does the ketogenic diet affect blood sugar levels?
The ketogenic diet can stabilize blood sugar levels by reducing carbohydrate intake, which is the primary source of glucose in the body. When carbs are limited, the body enters ketosis and begins to use fat for energy instead. This can lead to lower and more stable blood sugar levels for many individuals, particularly those with insulin sensitivity or type 2 diabetes. However, each person’s response may vary, and regular monitoring is crucial.
3. Are there risks of developing diabetes while on a keto diet?
While the ketogenic diet can be beneficial for many, there are some risks associated with it. For individuals prone to insulin resistance or those who consume excessive saturated fats, there could be an increased risk of metabolic disorders. Additionally, if not properly managed, the diet can lead to nutrient deficiencies that may contribute to other health issues. Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider can help mitigate these risks.
4. Can keto help reverse type 2 diabetes?
Some research suggests that the ketogenic diet can help reverse type 2 diabetes in some individuals by promoting weight loss, improving insulin sensitivity, and lowering blood sugar levels. However, this is not a guaranteed outcome for everyone. Each person’s health condition is unique, and a healthcare professional should be consulted to tailor a plan that works best for individual needs.
5. What should I consider before starting a ketogenic diet if I’m concerned about diabetes?
Before starting a ketogenic diet, especially if you have concerns about diabetes, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian. They can help assess your individual health status, recommend appropriate macronutrient ratios, and monitor your progress. Additionally, consider factors such as your current health conditions, medications, and lifestyle to ensure that the diet is safe and effective for you.
References
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7078145/
- https://www.diabetes.org/healthy-living/food-nutrition/understanding-carbohydrates
- https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/keto-diet-and-diabetes
- https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/basics/type2.html
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/health-information/nutrition-and-healthy-eating/keto-diet
- https://www.jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/2765120
- https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/nutritionsource/keto-diet/


