Kombucha can be keto-friendly, but it depends on the specific brand and type. While traditional kombucha tends to contain sugar from fermentation, many low-carb options are now available. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore how to choose the right kombucha for a ketogenic diet, its potential benefits, and what to watch out for, ensuring that you can enjoy this fermented beverage without compromising your health goals.
Understanding Kombucha and Its Ingredients

Kombucha is a fermented tea drink made by combining sweetened tea with a culture of bacteria and yeast, known as a SCOBY (Symbiotic Culture of Bacteria and Yeast). During the fermentation process, the yeast consumes the sugars in the tea, producing alcohol and carbon dioxide, while the bacteria convert the alcohol into acetic acid, giving kombucha its characteristic tangy flavor. However, this process can also leave residual sugars in the final product, which can be a concern for those following a ketogenic diet.
The ingredients in kombucha typically include tea, sugar, water, and the SCOBY. While the tea provides antioxidants and other beneficial compounds, the sugar is essential for fermentation but can lead to higher carbohydrate counts in the final drink. It’s crucial for keto dieters to be aware of the sugar content in kombucha, as this can significantly impact daily carbohydrate intake.
Nutritional Profile of Kombucha
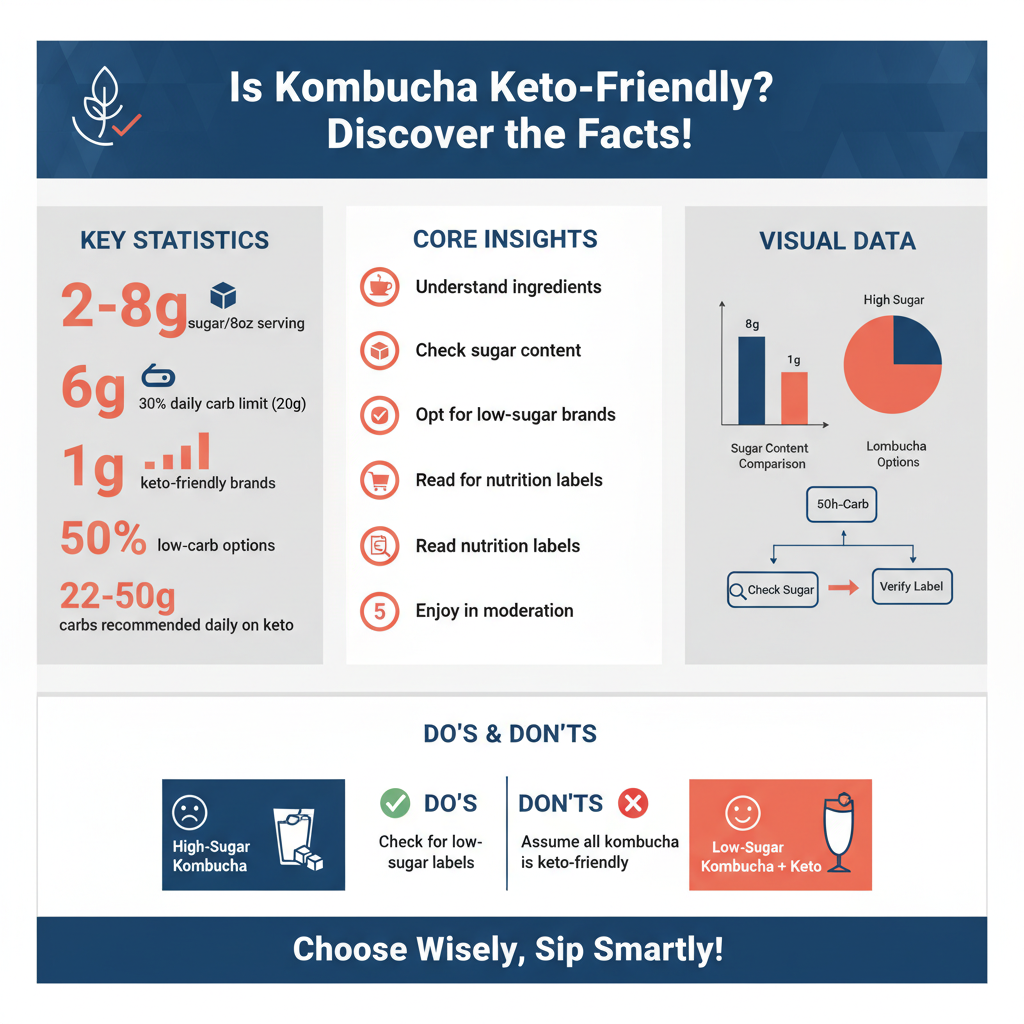

A typical serving of kombucha can have anywhere from 2 to 8 grams of sugar, depending on the brand and fermentation time. This sugar content can affect your carb intake on a keto diet, which generally limits daily carbohydrate consumption to around 20-50 grams. For example, a standard 8-ounce serving of many commercially available kombucha brands may contain 6 grams of sugar, which could take up a significant portion of your carb allowance for the day.
Fortunately, the market has seen a rise in low-sugar or zero-sugar kombucha options, making them more suitable for keto dieters. Brands like Health-Ade and GT’s Kombucha offer varieties that contain as little as 1 gram of sugar per serving, appealing to those who wish to enjoy kombucha without derailing their keto goals. Always check the nutrition label to ensure that the kombucha aligns with your carbohydrate limits.
How to Choose Keto-Friendly Kombucha
To select a keto-friendly kombucha, it is essential to look for brands that specifically label their drinks as low-carb or keto-friendly. This labeling indicates that the product has been formulated to minimize sugar and carbohydrate content. Additionally, always check the nutrition label for total sugars and carbohydrates per serving to ensure they fit within your daily limits.
When examining the ingredients list, opt for kombucha made from organic ingredients without added sugars or artificial sweeteners. Some brands use natural flavorings and sweeteners that can elevate the carb count, so scrutinizing the label is critical. Moreover, consider the fermentation time; longer fermentation periods typically result in lower sugar content, as more sugars are consumed by the yeast and bacteria.
Benefits of Kombucha on a Keto Diet
Incorporating kombucha into a keto diet can offer several health benefits. One of the primary advantages is its probiotic content, which can aid digestion and support gut health. A healthy gut is crucial for anyone on a restrictive diet, as it ensures proper nutrient absorption and can help alleviate digestive issues that may arise.
Furthermore, kombucha is often seen as a low-calorie alternative to sugary beverages, providing a flavorful option to satisfy cravings without the added sugars. The effervescence of kombucha can mimic the experience of drinking soda, making it a refreshing choice while maintaining hydration. Additionally, the antioxidants present in kombucha can help combat oxidative stress, contributing to overall health.
Potential Risks of Kombucha on Keto
Despite its benefits, there are potential risks associated with kombucha consumption on a ketogenic diet. One of the primary concerns is that some kombucha may still contain higher-than-expected sugars, which could kick you out of ketosis. This is particularly true for unflavored kombucha varieties that are not specifically designed to be low-carb. It’s essential to maintain vigilance and monitor your intake to avoid accidentally exceeding your carbohydrate limits.
Another consideration is caffeine sensitivity. Kombucha is made from tea, which naturally contains caffeine. If you are sensitive to caffeine or wish to limit your intake, be cautious about the type of tea used in the kombucha. Some brands may use high-caffeine teas, which could lead to increased heart rate or anxiety for sensitive individuals.
Alternatives to Traditional Kombucha
For those who want to control the ingredients and fermentation process, making your own kombucha at home is an excellent alternative. Home brewing allows you to customize the sugar content and flavor profile, ensuring that the final product aligns with your dietary needs. There are numerous online resources and kits available to help beginners get started with home brewing.
If kombucha does not fit well within your keto lifestyle, consider exploring other fermented beverages like kefir or low-sugar sodas. Kefir, a fermented milk drink, is rich in probiotics and can be made with minimal added sugars. Additionally, various brands now offer low-sugar sodas that provide a fizzy alternative without the high carb count associated with traditional sugary drinks.
In conclusion, kombucha can be keto-friendly if you choose the right products and monitor your sugar intake. Opt for low-sugar versions to enjoy the health benefits without compromising your diet. For those looking to incorporate kombucha into their keto lifestyle, always read labels carefully and consider homemade options for better control over ingredients. Embrace the balance of enjoying this unique beverage while staying aligned with your health and wellness goals.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is kombucha keto-friendly?
Yes, kombucha can be keto-friendly, but it largely depends on the specific brand and flavor. Traditional kombucha contains some sugars from the fermentation process, which can add carbohydrates. When choosing kombucha on a keto diet, look for options labeled as low-sugar or check the nutrition label to ensure the total carbohydrates align with your daily macros.
How many carbs are in a typical serving of kombucha?
A typical serving of kombucha (about 8 ounces) can contain anywhere from 2 to 8 grams of carbohydrates. This variation is due to the fermentation process and added ingredients like fruit or flavorings. For those on a keto diet, it’s essential to select brands that provide clear nutritional information and opt for those with lower carbohydrate content.
What should I look for in kombucha to ensure it’s suitable for a keto diet?
When selecting kombucha for a keto diet, prioritize those with low sugar and carbohydrate content. Look for labels that specify “1 gram of sugar” or “low-carb” to ensure they fit your dietary needs. Additionally, organic and naturally fermented options without added sweeteners or artificial flavors are preferable for maintaining keto compliance.
Why is the sugar content in kombucha important for a keto diet?
The sugar content in kombucha is crucial for a keto diet because excess sugar can hinder your ability to maintain ketosis, the metabolic state where your body burns fat for fuel instead of carbohydrates. Since the keto diet typically limits daily carbohydrate intake to about 20-50 grams, even a seemingly small amount of sugar in kombucha can impact your overall carb count for the day.
Which brands of kombucha are best for a keto diet?
Some popular kombucha brands that offer keto-friendly options include GT’s Enlightened Kombucha, Health-Ade Kombucha, and Humm Kombucha. These brands often provide a range of flavors with lower sugar content, making them suitable for keto enthusiasts. Always check the nutrition labels to verify the carbohydrate content before purchasing.
References
- Kombucha
- https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/kombucha
- https://www.webmd.com/diet/obesity/kombucha-what-you-need-to-know
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7011534/
- https://www.verywellfit.com/kombucha-and-the-keto-diet-4788858
- Psoriasis oral medication: Types, uses, and side effects
- https://www.health.harvard.edu/staying-healthy/the-health-benefits-of-kombucha
- Home – The Microsetta Initiative
- https://www.cdc.gov/foodsafety/communication/kombucha.html


