A ketogenic diet typically consists of around 70-80% of daily calories coming from fat, which translates to approximately 150-200 grams of fat per day for many individuals. This high-fat intake is essential for achieving and maintaining ketosis, the metabolic state where the body burns fat for fuel. The keto diet is designed to shift your body from relying on carbohydrates as its primary energy source to utilizing fat, making the understanding of fat consumption critical. In this article, we’ll explore the specific fat requirements on a keto diet, the types of fats to include, and how to track your intake effectively.
Understanding Macronutrient Ratios in Keto

To fully grasp the significance of fat intake on a ketogenic diet, it is important to understand the standard macronutrient breakdown. A typical keto diet consists of approximately 70-80% fats, 20-25% proteins, and only 5-10% carbohydrates. This specific balance is crucial for initiating and maintaining ketosis. By significantly reducing carbohydrate intake, the body depletes its glycogen stores and begins to burn fat for energy instead.
Maintaining these ratios is essential for several reasons. Firstly, by adhering to a high-fat, low-carb diet, you enable your body to enter ketosis more quickly, which can lead to rapid weight loss and improved metabolic health. Secondly, consistent adherence to these macronutrient ratios can help mitigate the common “keto flu,” a temporary set of symptoms some individuals experience when transitioning to a ketogenic lifestyle. Thus, understanding and managing your macronutrient ratios is vital for anyone looking to succeed on a keto diet.
The Role of Fats in a Keto Diet
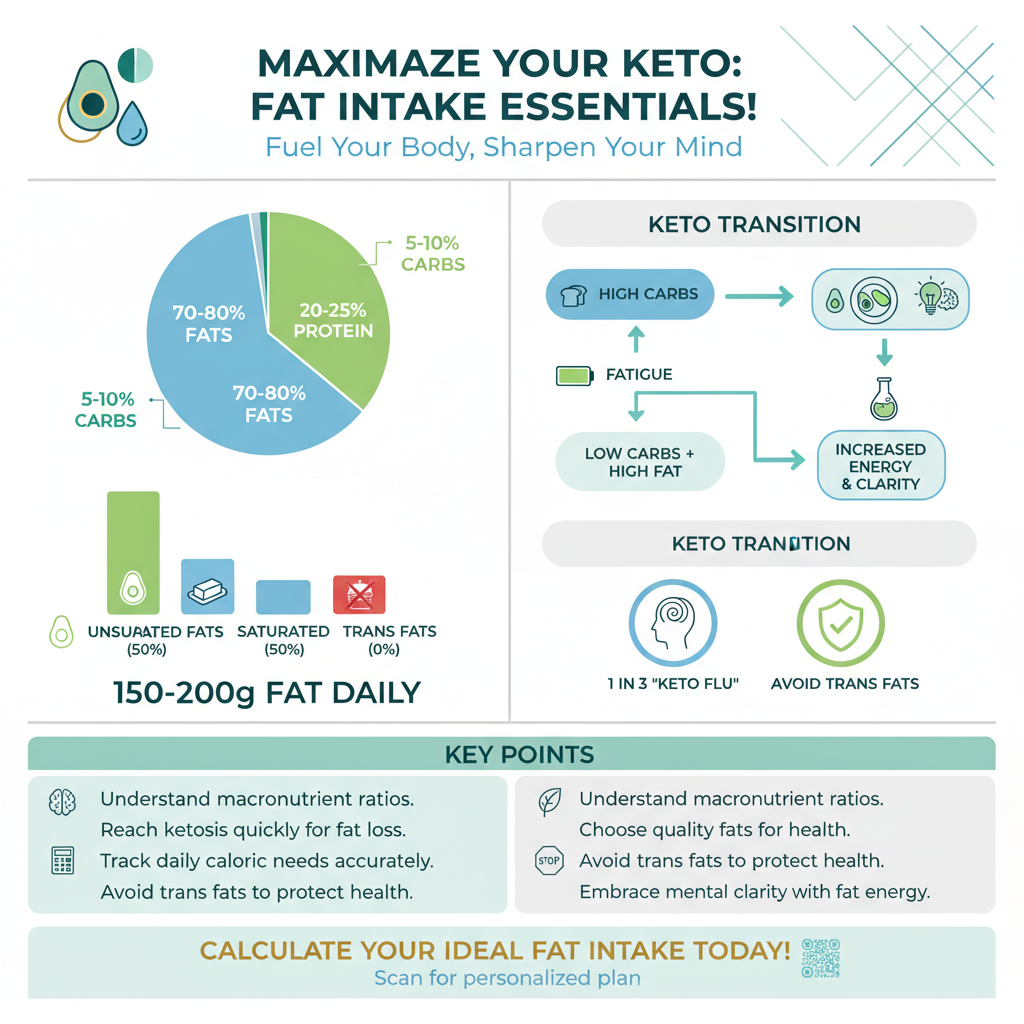

Fats serve as the primary energy source in a ketogenic diet, replacing carbohydrates that are typically used for fuel. In a state of ketosis, the liver converts fatty acids into ketones, which then serve as an alternative energy source for the brain and body. This metabolic shift not only aids in fat loss but also enhances mental clarity and energy levels.
When it comes to the types of fats consumed, quality matters. Fats can be categorized into three main types: saturated, unsaturated, and trans fats. Saturated fats, such as those found in coconut oil and butter, can be beneficial in moderation. Unsaturated fats, including those from avocados, olive oil, and fatty fish, are considered heart-healthy and should form the bulk of your fat intake. Conversely, trans fats, commonly found in processed foods, should be avoided as they can lead to various health issues.
Calculating Your Daily Fat Intake
Determining your daily caloric needs is the first step in calculating your fat intake on a ketogenic diet. This calculation is influenced by several factors, including your weight, age, activity level, and personal health goals. For example, if your maintenance calorie requirement is 2,000 calories per day, and you aim for a target of 75% of total calories from fat, you would need to consume approximately 1,500 calories from fat. Since every gram of fat contains about 9 calories, this translates to roughly 167 grams of fat daily.
To accurately calculate your specific fat intake, it’s advisable to use a macronutrient calculator or consult with a nutritionist. They can provide personalized recommendations based on your unique situation, ensuring you meet your dietary goals while adhering to the ketogenic framework.
Types of Fats to Include
Incorporating the right types of fats is essential for a successful ketogenic diet. Healthy fats not only provide energy but also offer various health benefits. Some excellent sources of healthy fats include:
– Avocados: Rich in monounsaturated fats and fiber, avocados are versatile and nutritious.
– Nuts: Almonds, walnuts, and macadamia nuts are great for snacking and offer healthy fats along with protein.
– Olive Oil: Extra virgin olive oil is a staple in Mediterranean diets and is celebrated for its anti-inflammatory properties.
– Fatty Fish: Salmon, mackerel, and sardines are high in omega-3 fatty acids, which support heart health.
On the other hand, certain fats should be avoided to maintain overall health. Trans fats, often found in margarine and many processed snacks, can increase bad cholesterol levels and are linked to various health problems. Additionally, heavily processed oils, such as soybean and corn oil, should be minimized as they can disrupt the balance of omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids in the diet.
Tracking Your Fat Intake
Monitoring your daily fat intake is crucial for ensuring you stay within your desired macronutrient ratios. Several tools and apps can assist in tracking your food consumption effectively. Popular options include MyFitnessPal, Cronometer, and Carb Manager, which allow you to log meals and analyze nutrient breakdown in real-time.
Understanding food labels is also essential when managing fat intake. Always check serving sizes, types of fats included, and the overall caloric content. By being vigilant about portion sizes and food quality, you can maintain better control over your dietary fat consumption.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
While embarking on a ketogenic diet, individuals often make several common mistakes. One of the most prevalent issues is overestimating or underestimating fat consumption. It’s easy to assume that all fats are good, but failing to balance fat intake with proteins and carbohydrates can lead to nutritional deficiencies or inadequate energy levels.
Another mistake is neglecting to account for hidden carbohydrates in certain high-fat foods, which can inadvertently push you out of ketosis. Always be mindful of the total carbohydrate content in the foods you consume, especially those labeled as “keto-friendly.”
Tips for Maintaining a Balanced Keto Diet
Successful adherence to a ketogenic diet often hinges on effective meal planning and preparation. By organizing your meals in advance, you can ensure you meet your fat goals while incorporating a variety of nutrient-dense foods. Consider preparing meals that combine various sources of healthy fats, like a salad topped with olive oil, avocado, and nuts.
Incorporating a diverse range of fats not only enhances the flavor of your dishes but also optimizes nutritional benefits. For example, combine fatty fish with a side of sautéed leafy greens in olive oil for a well-rounded meal. Staying engaged with your food choices will make the diet more enjoyable and sustainable.
By understanding the fat requirements of a keto diet, you can tailor your meals to meet your health and weight loss goals effectively. Focus on the quality of fats you consume, track your intake diligently, and adjust as necessary. If you’re ready to dive deeper into your keto journey, consider engaging with a nutritionist or exploring keto meal planning resources. Ultimately, a well-planned ketogenic diet can lead to remarkable improvements in overall health and well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
How many grams of fat should I eat on a keto diet?
On a ketogenic diet, the general guideline is to consume approximately 70-80% of your daily calories from fat. For most individuals, this translates to about 150-200 grams of fat per day, depending on total caloric intake and personal goals. It’s essential to tailor your fat intake to your individual energy needs and weight loss objectives, while also focusing on healthy fat sources like avocados, nuts, and olive oil.
Why is fat consumption important in a keto diet?
Fat consumption is crucial in a keto diet because it serves as the primary source of energy when carbohydrates are restricted. By consuming high amounts of fat, your body enters a metabolic state called ketosis, where it burns fat for fuel instead of carbs. This shift not only aids in weight loss but also stabilizes blood sugar levels and supports overall health when paired with nutrient-dense foods.
What types of fats are best for a keto diet?
The best types of fats for a keto diet include monounsaturated fats like olive oil and avocado oil, saturated fats from sources like coconut oil and grass-fed butter, and omega-3 fatty acids found in fatty fish and flaxseeds. These healthy fats not only promote ketosis but also provide essential nutrients and support heart health. Avoid trans fats and highly processed oils, as they can negatively impact your health.
How do I calculate my daily fat intake on a keto diet?
To calculate your daily fat intake on a keto diet, first determine your total daily caloric needs based on your age, weight, activity level, and goals. From there, multiply your caloric intake by 0.70 to 0.80 (for 70-80% fat) to find the number of calories that should come from fat. Since each gram of fat contains 9 calories, divide the total fat calories by 9 to find the number of grams of fat you should aim for daily.
Which common mistakes should I avoid regarding fat intake on a keto diet?
Common mistakes to avoid include not consuming enough healthy fats, which can hinder your ability to enter ketosis, or relying too heavily on unhealthy fats like processed oils and trans fats. Additionally, some people mistakenly believe that any fat is acceptable on a keto diet, leading to an imbalanced nutrient intake. It’s important to focus on whole food sources of fat and balance your diet with adequate protein and low-carb vegetables for optimal health results.


