Staying on the keto diet can vary from person to person, but generally, it is advisable to follow it for at least three to six months for optimal results. This timeframe allows your body to adapt fully to ketosis and achieve weight loss or health goals. As you embark on your keto journey, understanding the implications of this dietary approach is crucial, as it can significantly influence your overall health and lifestyle. In this article, we will explore the factors influencing how long you might stay on the keto diet, signs that indicate it’s time to transition, and tips for maintaining long-term health.
Understanding the Keto Diet

The ketogenic diet is a low-carb, high-fat diet designed to encourage ketosis, a metabolic state where the body burns fat for fuel instead of carbohydrates. Typically, the diet involves drastically reducing carbohydrate intake—often to less than 50 grams per day—and replacing it with healthy fats, which can constitute around 70-80% of your total calorie intake. This shift in macronutrient ratios prompts the liver to convert body fat into ketones, which serve as an alternative energy source.
The keto diet has gained popularity not only for weight loss but also for potential health benefits, including improved blood sugar control, enhanced mental clarity, and even reduced inflammation. However, it is essential to approach the diet with careful planning and an understanding of how it may affect your body over time.
Factors Influencing Duration on Keto
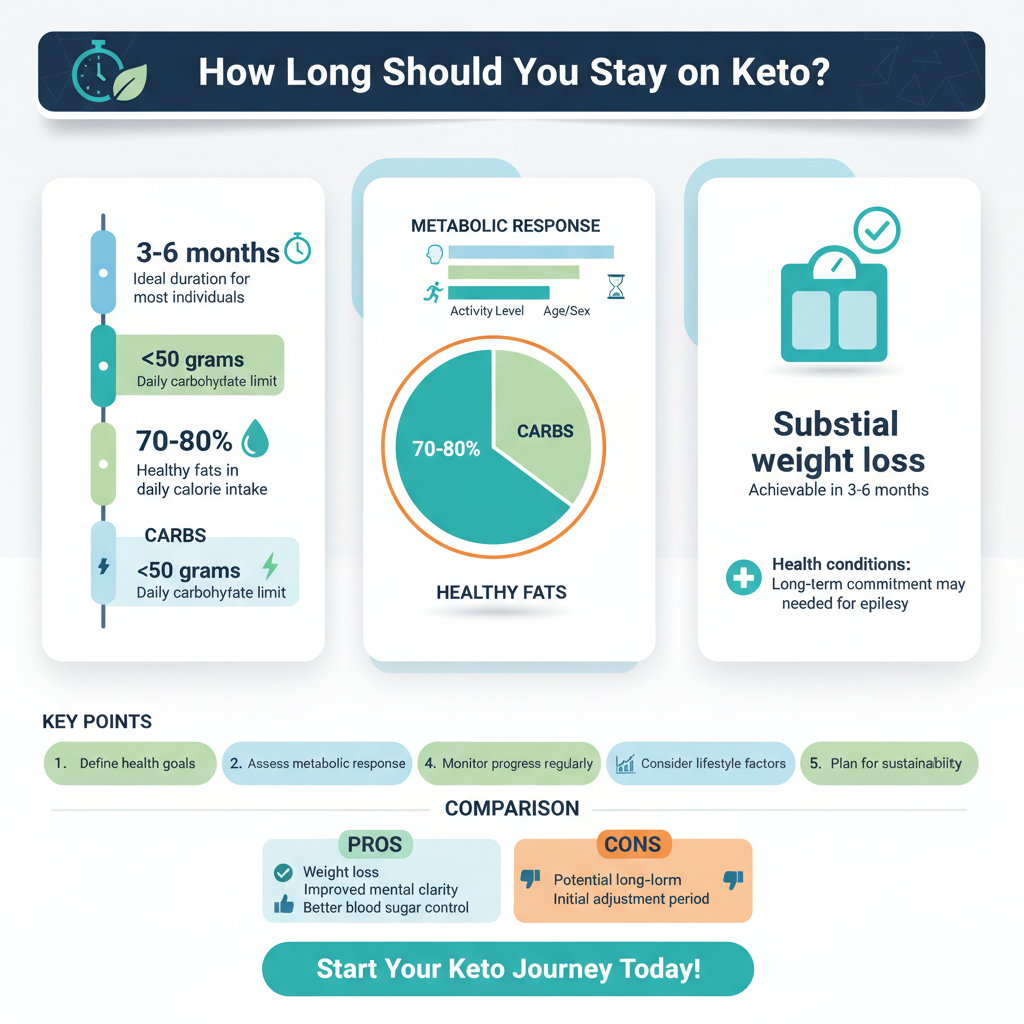

Several factors can influence how long an individual should remain on the keto diet.
– Individual health goals: Your specific objectives play a significant role in determining the duration of your keto journey. For instance, individuals aiming for substantial weight loss may find three to six months effective in shedding pounds, while those with conditions like epilepsy may require a long-term commitment to manage their symptoms effectively.
– Metabolic response: Each person’s metabolic rate varies, meaning that some may enter ketosis more quickly than others. Factors such as age, sex, activity level, and overall health can impact how rapidly you achieve and maintain ketosis. For example, a younger individual with a higher metabolic rate may transition into ketosis in a matter of days, while others may take weeks.
Understanding these factors can help tailor your keto experience to your unique needs. Regularly assessing your progress and reassessing your goals can optimize your approach and help you decide when it may be time to transition to a different dietary plan.
Signs You Might Need to Transition
Recognizing when to transition off the keto diet is vital for maintaining optimal health. Here are some signs that it may be time to reconsider your keto commitment:
– Persistent fatigue or a lack of energy: If you consistently feel drained, even after achieving ketosis, it could indicate that your body is not responding well to the diet. This fatigue may stem from inadequate caloric intake or nutrient imbalances, suggesting a need for dietary adjustment.
– Nutrient deficiencies: Long-term adherence to the keto diet without proper management can lead to deficiencies in essential vitamins and minerals, such as magnesium, potassium, and certain B vitamins. Symptoms of these deficiencies can include muscle cramps, fatigue, and cognitive decline. Regular blood tests can help monitor nutrient levels and identify any concerns.
Listening to your body and being aware of these signs is crucial in deciding whether to continue on the keto diet or explore a more balanced approach.
Short-term vs. Long-term Keto
The duration on the keto diet can generally be categorized into short-term and long-term approaches:
– Short-term (3-6 months): This is an ideal timeframe for individuals looking to kickstart weight loss or significantly improve their health markers. A focused, short-term keto diet can help reset your metabolism, improve insulin sensitivity, and lead to rapid weight loss. However, it is recommended to incorporate a more balanced diet afterward to ensure sustainable health.
– Long-term (beyond 6 months): Some individuals may choose to stay on the keto diet for extended periods. While this is possible, it requires careful management to avoid potential health issues such as liver problems, kidney stones, or nutrient deficiencies. If you opt for a longer duration, consider cycling in and out of ketosis or incorporating periodic carbohydrate re-feeds to maintain metabolic flexibility and overall health.
Understanding the implications of both approaches can help you strategize your dietary plan for the best results.
Tips for a Successful Keto Journey
To ensure a successful experience on the keto diet, consider the following tips:
– Monitor your health: Regular check-ups with healthcare professionals can help catch any negative side effects early on. Blood tests can provide insight into your nutrient levels, liver function, and overall metabolic health.
– Stay flexible: While adhering strictly to keto can yield results, consider incorporating flexibility into your plan. Cycling on and off the diet, or occasionally reintroducing healthy carbohydrates, can help mitigate the risk of nutrient deficiencies and promote a balanced lifestyle post-keto.
– Educate yourself: Stay informed about the keto diet and its potential impacts on your body. Understanding how different foods affect your state of ketosis can empower you to make healthier choices.
By employing these strategies, you are more likely to achieve your health goals while minimizing potential risks associated with long-term keto adherence.
Alternatives After Keto
Transitioning off the keto diet can be as important as the initial commitment. Here are some alternatives to consider:
– Transitioning to a balanced diet: Gradually reintroducing healthy carbohydrates, such as whole grains, fruits, and legumes, can help maintain energy levels while still emphasizing whole, unprocessed foods. Focus on a balanced intake of macronutrients to support overall health.
– Exploring other dietary approaches: After keto, you may wish to explore other dietary plans that align with your long-term health and lifestyle goals. For example, the Mediterranean diet emphasizes healthy fats, lean proteins, and a variety of fruits and vegetables, making it a sustainable option for many.
By thoughtfully transitioning away from keto, you can continue to enjoy the benefits of improved health while expanding your dietary horizons.
In summary, staying on the keto diet typically ranges from three to six months, depending on individual goals and health responses. It’s essential to listen to your body and recognize when it’s time to transition. For those considering or currently on the keto diet, take the time to monitor your health and explore alternatives that promote sustained wellness. If you have further questions about the keto diet or need personalized advice, consult a healthcare professional or a nutritionist.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long can you safely stay on the keto diet?
While the keto diet can be effective for weight loss and other health benefits, it’s generally recommended to follow it for a period of 3 to 6 months. After this time, many individuals may benefit from a break or a transition to a more balanced diet to prevent nutrient deficiencies and promote metabolic flexibility. Consulting a healthcare professional can help tailor the duration to your individual health goals and needs.
What are the signs that you should stop the keto diet?
Signs that you may need to stop the keto diet include persistent fatigue, digestive issues, nutrient deficiencies, or feeling excessively restricted. If you experience any negative side effects such as keto flu symptoms or an inability to maintain your energy levels, it may be time to reassess your dietary approach. Listening to your body and consulting with a nutritionist can provide clarity on whether to continue or adjust your diet.
Why do people choose to cycle on and off the keto diet?
Many individuals opt to cycle on and off the keto diet to avoid metabolic slowdown and potential nutrient deficiencies that can arise from a prolonged state of ketosis. Cycling allows the body to reset and can improve adherence by incorporating more variety in the diet. This approach can also help mitigate feelings of deprivation and encourage a more sustainable, long-term healthy eating pattern.
How do I know if the keto diet is right for me in the long term?
Determining if the keto diet is suitable for you long-term involves assessing your health goals, lifestyle, and how your body responds to the diet. If you find that you’re enjoying the diet, feeling energized, and achieving your health goals without adverse effects, it may be a good fit. However, if you experience negative side effects or find the diet overly restrictive, it might be beneficial to explore other dietary options that align better with your lifestyle and preferences.
What is the best way to transition off the keto diet?
The best way to transition off the keto diet is to gradually reintroduce carbohydrates while monitoring how your body reacts. Start with small portions of whole, nutrient-dense carbs such as fruits, whole grains, and starchy vegetables. This slow reintroduction can help prevent sudden weight gain and support metabolic adaptation, ensuring a smoother transition back to a more balanced diet.
References
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8535748/
- https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/keto-diet-what-to-know
- https://www.reuters.com/article/us-health-ketogenic-diet-idUSKBN2A10Y8
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/nutrition-and-healthy-eating/expert-answers/keto-diet/faq-20457251
- https://www.webmd.com/diet/obesity/keto-diet-overview
- https://www.nutrition.gov/topics/whats-nutrition/nutrition-education/keto-diet
- Diet Review: Ketogenic Diet for Weight Loss • The Nutrition Source
- https://www.eatright.org/health/dietary-guidelines-and-myplate/nutrition-basics/the-ketogenic-diet


