The duration for following the keto diet varies significantly based on individual health goals, lifestyle, and personal preferences. While many people commit to a strict ketogenic regimen for 3 to 6 months to achieve notable weight loss or improve specific health markers, others may adopt a more flexible approach for a longer period. This article will delve into the optimal duration for the keto diet, considering various influencing factors and personal circumstances.
Understanding the Keto Diet Duration

The ketogenic diet is characterized by a high-fat, moderate-protein, and very low-carbohydrate intake that aims to induce a state of ketosis in the body. During ketosis, the body shifts its primary energy source from glucose to ketones, derived from fat. To experience the initial benefits of the keto diet, adherence for at least a few weeks is generally recommended. During this period, individuals can expect to see a reduction in cravings, an increase in energy levels, and a boost in mental clarity.
For some, remaining in ketosis for months or even years can be beneficial, particularly if they are managing chronic health conditions such as epilepsy or type 2 diabetes. However, the sustainability of such a regimen often depends on individual factors, including metabolic response, lifestyle, and personal goals. Thus, while the keto diet can be an effective short-term strategy, its long-term implementation requires careful consideration and planning.
Factors Influencing Duration
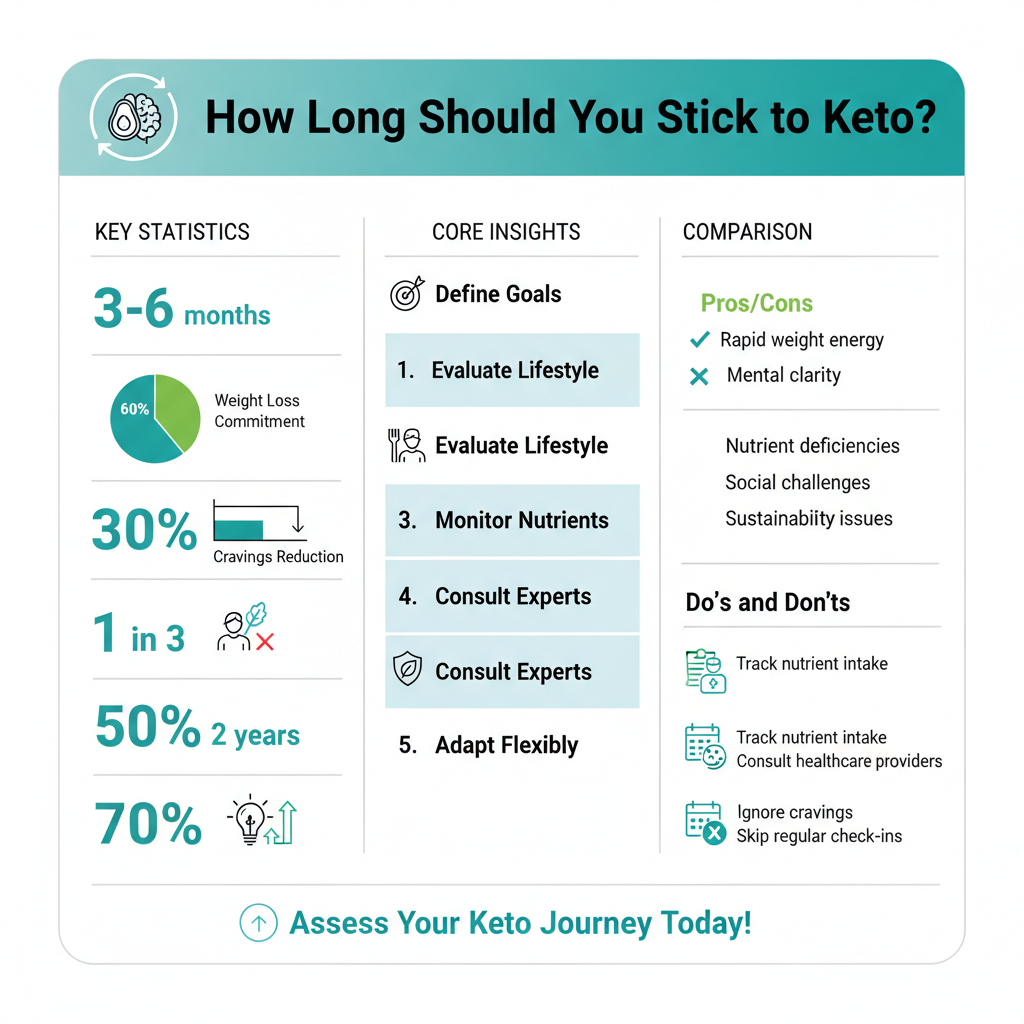

Several key factors influence how long an individual should follow the keto diet.
1. Individual Health Goals: Your specific objectives can greatly dictate the duration of your keto journey. For instance, those aiming for significant weight loss may find a short-term commitment of 3 to 6 months particularly effective. Conversely, individuals seeking to manage conditions like insulin resistance or metabolic syndrome might benefit from a more extended period on the diet.
2. Personal Lifestyle: Dietary preferences and lifestyle habits also play a crucial role in determining how sustainable the keto diet is for you. If you enjoy a diverse range of foods and social dining experiences that include carbohydrates, the rigid structure of traditional keto may not be long-term viable. For those who thrive on routine and enjoy high-fat meals, a longer adherence could be achievable.
3. Nutritional Considerations: The ketogenic diet can sometimes lead to nutrient deficiencies if not properly managed. As such, individuals must consider their overall nutritional intake and how long they can maintain a well-rounded diet while adhering to strict macronutrient ratios. Consulting with a healthcare provider or a registered dietitian can help tailor dietary choices to meet nutritional needs.
Short-Term vs. Long-Term Keto
Engaging in a short-term keto diet can yield rapid weight loss and significant metabolic changes. Many individuals report initial weight loss due to the loss of water weight and a reduction in hunger, as fat becomes the primary energy source. This phase can be particularly motivating and may lead to improved metrics on health markers, such as blood sugar and cholesterol levels, within the first few months.
However, long-term adherence to the keto diet may lead to additional health benefits, including enhanced mental clarity, sustained energy levels, improved blood sugar control, and potential reductions in inflammation. Nevertheless, maintaining a long-term ketogenic lifestyle necessitates careful management to prevent nutrient deficiencies, as it can limit the intake of certain vitamins and minerals typically found in carbohydrate-rich foods like fruits and whole grains.
For individuals who wish to pursue long-term keto, it may be wise to incorporate strategies to enhance dietary variety or consider a more flexible approach, such as cyclical or targeted keto.
Signs It Might Be Time to Stop
Listening to your body is crucial when it comes to determining how long to stay on the keto diet. There are several signs that may indicate it’s time to re-evaluate your dietary choices:
1. Adverse Effects: If you begin to experience negative side effects such as digestive issues (bloating, constipation), fatigue, or mood swings, it might be a signal to transition off the keto diet or modify your approach. These symptoms could indicate that your body is not responding well to the dietary changes.
2. Reaching Goals: Once you have achieved your initial health or weight loss goals, this might be an appropriate time to consider a transition period. Gradually reintroducing carbohydrates can help you assess how your body reacts and adapt to a more balanced diet, ensuring that you maintain your health improvements without reverting to old habits.
Transitioning Off the Keto Diet
Transitioning off the keto diet should be done gradually to allow your body to adjust to the reintroduction of carbohydrates. This process can minimize the risk of weight regain and metabolic disruptions.
1. Gradual Carbohydrate Reintroduction: Start by adding small amounts of healthy carbohydrates, such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, to your meals. Monitor your body’s response to these changes, adjusting as necessary to avoid any negative side effects.
2. Balanced Diet Maintenance: After the keto diet, it is essential to focus on maintaining a balanced diet to ensure nutrient adequacy. Prioritize whole foods, including a variety of macronutrients, vitamins, and minerals to support overall health. Consulting with a registered dietitian during this transition can provide valuable guidance.
Expert Opinions and Research
Experts in nutrition often emphasize the importance of personalizing the duration of the keto diet based on individual responses and lifestyle factors. Research has shown that while short-term keto can be effective for weight loss and certain health improvements, long-term success is frequently linked to dietary flexibility.
For example, a study published in the journal “Nutrition” indicated that individuals who incorporate flexibility into their dietary choices are more likely to maintain weight loss and overall health in the long run. This suggests that a rigid adherence to the keto diet may not be necessary or beneficial for everyone, and that a more adaptable approach can yield better results.
Alternatives to Long-Term Keto
For individuals seeking alternatives to long-term strict keto, exploring cyclical or targeted keto strategies can provide a sustainable option.
1. Cyclical Keto: This approach involves alternating between periods of strict keto and higher-carb days, allowing for a diverse diet while still reaping the benefits of ketosis.
2. Targeted Keto: For those engaged in high-intensity exercise, targeted keto involves consuming carbohydrates around workouts to provide energy while maintaining a ketogenic state.
3. Other Dietary Plans: Additionally, considering other dietary patterns, such as a Mediterranean diet or a balanced whole-foods approach, can align with personal goals and lifestyle, emphasizing nutrient-rich foods without strict macronutrient limitations.
In summary, the duration of the keto diet varies widely among individuals based on specific health goals and lifestyle factors. Whether you opt for a short-term or long-term approach, it is essential to listen to your body and consult healthcare professionals as needed. If you’re contemplating starting or adjusting your keto journey, take the time to assess your goals and make informed decisions that align with your health and well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long should you stay on the keto diet for optimal results?
The duration of the keto diet can vary significantly based on individual goals, but many people find success with a commitment of at least 3 to 6 months to see noticeable weight loss and health benefits. It’s essential to evaluate your progress regularly and consult with a healthcare professional to determine if you should continue or modify your approach based on your personal health and weight-loss goals.
What are the signs that indicate I should stop the keto diet?
If you experience persistent side effects such as fatigue, digestive issues, or nutrient deficiencies, it may be time to reassess your keto diet. Additionally, if you have reached your weight loss goals or if the diet is negatively affecting your mental or physical well-being, consider transitioning to a more sustainable eating plan that incorporates a wider variety of foods while still maintaining low carbohydrate intake.
Why do some people only do keto for a short time?
Many individuals opt for short-term keto diets to jumpstart weight loss or to achieve specific health goals, such as improving insulin sensitivity or reducing inflammation. While a brief period on the keto diet can yield quick results, sustaining such a low-carb lifestyle long-term may be challenging for some due to cravings or social situations, prompting them to return to a more balanced diet after achieving initial success.
What is the best way to transition off the keto diet after a long-term commitment?
Transitioning off the keto diet should be done gradually to avoid potential side effects like the “keto flu.” Start by slowly reintroducing carbohydrates, focusing on nutrient-dense options such as whole grains, fruits, and legumes, while maintaining a moderate protein intake. Monitor your body’s response and adjust your macronutrient ratios as needed to find a balance that supports your health and weight management goals.
Which factors influence how long I should follow the keto diet?
Several factors can influence the duration of your keto diet, including your initial weight, health conditions, fitness goals, and individual metabolism. Personal preferences and lifestyle choices also play a significant role; if you find the strict dietary restrictions challenging, a shorter duration may be more beneficial. Ultimately, listening to your body and consulting with a healthcare professional can help you tailor your keto experience to meet your unique needs.
References
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6520670/
- https://www.webmd.com/diet/what-to-know-about-keto-diet
- https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/what-is-the-keto-diet
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/nutrition-and-healthy-eating/expert-answers/keto-diet/faq-20445286
- https://www.cdc.gov/healthyweight/assessing/bmi/adult_bmi/english_bmi_calculator/bmi_calculator.html
- https://www.nhs.uk/live-well/eat-well/the-ketogenic-diet/


