The keto diet can be followed safely for several months to years, depending on individual health conditions and dietary goals. Adhering to a ketogenic lifestyle can lead to significant weight loss and improved metabolic health, but the duration of this diet should be tailored to your specific needs and monitored closely. This article will explore the duration of the keto diet, factors influencing how long you can stay on it, and tips for maintaining a healthy lifestyle while following this popular eating plan.
Understanding the Keto Diet

The ketogenic diet is a high-fat, low-carbohydrate eating plan designed to shift the body into a metabolic state known as ketosis. In ketosis, the body becomes highly efficient at burning fat for energy due to the drastic reduction in carbohydrate intake. The typical macronutrient breakdown of the keto diet consists of approximately 70-80% fats, 15-25% protein, and only 5-10% carbohydrates. This significant decrease in carbohydrates forces the liver to convert fat into ketones, which serve as an alternative energy source for the brain and other tissues. As a result, many people experience weight loss, increased energy, and improved mental clarity shortly after beginning the diet. However, it is essential to approach the keto lifestyle with a comprehensive understanding of its principles and potential effects on the body.
Recommended Duration for the Keto Diet
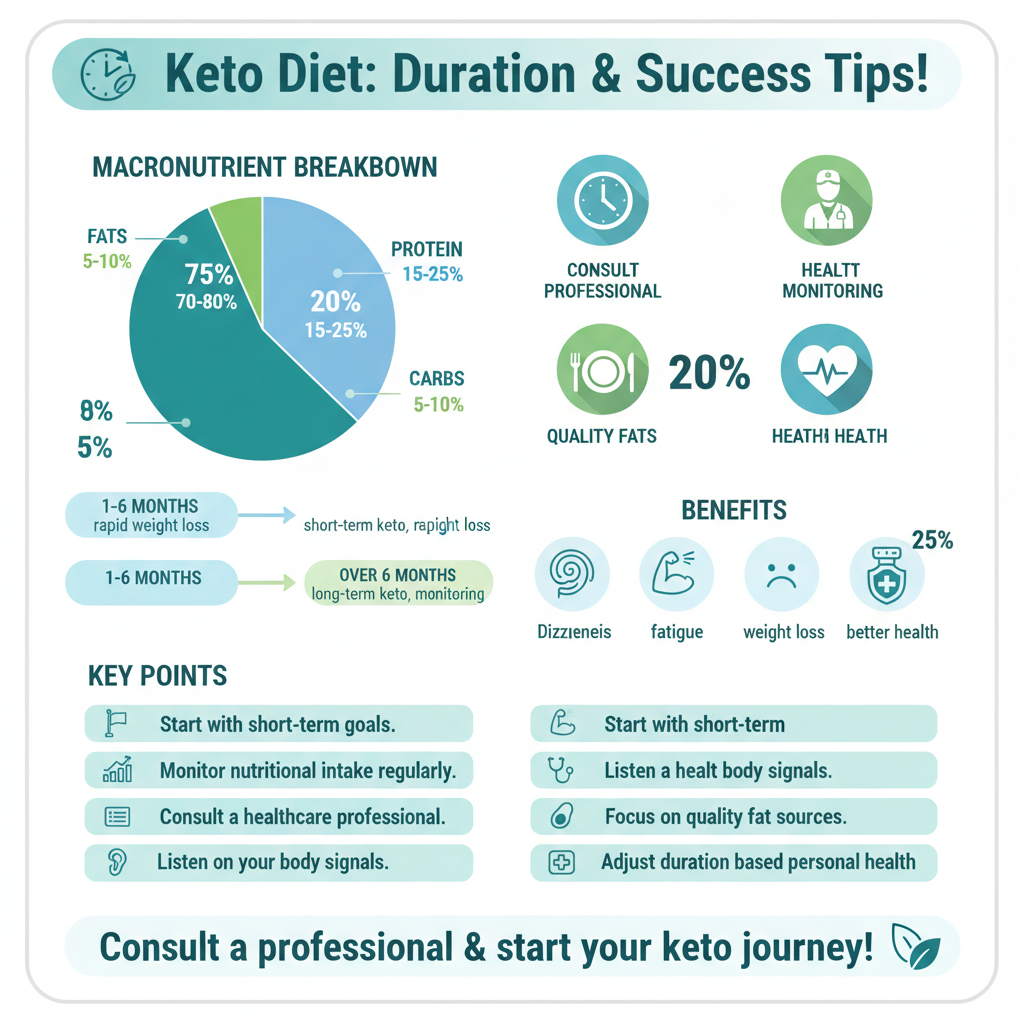

The duration for which individuals can safely follow the keto diet varies widely based on personal health goals and overall well-being. Short-term keto, typically ranging from 1 to 6 months, is often sufficient for individuals seeking rapid weight loss or metabolic benefits. Many people report significant improvements in body composition and energy levels during this period, making it an appealing choice for those looking to shed pounds quickly.
Conversely, long-term adherence to the keto diet—extending beyond 6 months—may require more careful monitoring. While some individuals may thrive on a long-term keto plan, others may experience adverse effects, including nutrient deficiencies due to the restricted range of foods. It is crucial to regularly evaluate nutritional intake and consult healthcare professionals to ensure that all essential vitamins and minerals are being consumed adequately. For example, focusing on high-quality fats from sources like avocados, nuts, and olive oil can help mitigate some deficiencies while on a prolonged keto diet.
Signs You Should Stop the Keto Diet
Listening to your body is critical when following the keto diet. There are specific signs that may indicate it’s time to reconsider your dietary choices. Persistent fatigue or brain fog are common indicators that the body may not be adjusting well to the high-fat, low-carb lifestyle. While some fatigue is to be expected during the initial transition, prolonged lethargy could suggest that your body is struggling to adapt.
Unexplained digestive issues, such as constipation or diarrhea, can also signal a need for dietary changes. These symptoms might stem from a lack of dietary fiber, which is often reduced on a keto diet due to the limited consumption of fruits and whole grains. If you experience these or similar symptoms, it may be wise to consult a healthcare professional and reassess your nutritional intake or consider modifying your approach to the diet.
Health Considerations for Long-Term Keto
Maintaining a long-term keto diet entails several health considerations that should not be overlooked. Regular health check-ups are essential to monitor cholesterol levels, kidney function, and overall metabolic health. While some studies suggest that the keto diet may improve cholesterol profiles in certain individuals, others may experience an increase in LDL cholesterol, which could pose cardiovascular risks.
Individuals with preexisting medical conditions, such as diabetes, liver disease, or pancreatic disorders, should consult a healthcare professional before initiating or continuing a ketogenic lifestyle. Tailored advice from a qualified practitioner can help optimize the diet while minimizing potential risks. For instance, those with diabetes may benefit from a keto diet that emphasizes high-quality, nutrient-dense foods while closely monitoring blood sugar levels.
Tips for Maintaining a Balanced Keto Diet
To successfully maintain a balanced keto diet, it is vital to incorporate a variety of low-carb vegetables into your meals. Vegetables such as leafy greens, broccoli, and cauliflower are not only low in carbohydrates but also packed with essential vitamins, minerals, and fiber. Ensuring a diverse intake of these foods can help prevent nutrient deficiencies and promote overall health.
Staying hydrated is another critical aspect of sustaining a keto lifestyle. Dehydration is a common concern, especially during the early stages of the diet. It is advisable to drink plenty of water and consider supplementing with electrolytes to manage symptoms associated with the “keto flu,” which can include headaches, fatigue, and muscle cramps. Consuming mineral-rich foods or electrolyte supplements can help alleviate these discomforts and support your body during the transition into ketosis.
Transitioning Off the Keto Diet
When it’s time to transition off the keto diet, it is essential to do so gradually to minimize the risk of rapid weight gain and other health complications. Reintroducing carbohydrates should be a slow process, allowing your body to adjust to the change in macronutrient composition. Start with small portions of whole, nutrient-dense carbohydrates, such as quinoa, sweet potatoes, or whole grains, and monitor your body’s response.
Focusing on whole foods and balanced meals is crucial in maintaining health benefits after leaving the keto diet. Aim to include a variety of food groups while being mindful of portion sizes. This approach not only helps in managing weight but also ensures that you continue to receive essential nutrients for long-term health.
In summary, the keto diet can be an effective weight loss and health improvement tool when followed correctly. The duration for which one can safely adhere to this diet varies, and it is crucial to listen to your body and consult with healthcare professionals. By considering individual health conditions and dietary goals, one can successfully navigate the keto lifestyle while maintaining overall well-being. Remember, transitioning off the diet should be done thoughtfully to sustain health benefits and avoid unwanted side effects.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long can you safely follow the keto diet?
The keto diet can be followed safely for a few months to several years, depending on individual health conditions and goals. Many people start with a 3 to 6-month duration to see significant weight loss and health improvements. However, maintaining a long-term ketogenic lifestyle might require periodic carb cycling or adjustments to prevent nutrient deficiencies and support metabolic health.
What are the potential side effects of being on the keto diet for a long time?
Long-term adherence to the keto diet may lead to side effects such as nutrient deficiencies, digestive issues, and potential impacts on heart health due to high saturated fat intake. It’s essential to monitor your health regularly and consult with a healthcare provider to ensure that you’re meeting your nutritional needs and addressing any side effects that arise from prolonged ketosis.
Why do some people stop the keto diet after a few weeks?
Many people discontinue the keto diet after a few weeks due to initial side effects such as the “keto flu,” which includes fatigue, headaches, and irritability during the transition to ketosis. Additionally, the restrictive nature of the diet can lead to cravings for carbohydrates and social pressure, making it difficult to maintain long-term. It’s crucial for those considering keto to have a solid understanding of the diet and strategies for overcoming these challenges.
What is the best way to transition off the keto diet?
The best way to transition off the keto diet is to gradually increase carbohydrate intake over a few weeks rather than reintroducing carbs all at once. Start by adding healthy carbs such as fruits, whole grains, and starchy vegetables while monitoring your body’s response. This gradual approach helps prevent weight regain and minimizes digestive distress, allowing your body to adjust smoothly back to a higher carbohydrate diet.
Which foods should you avoid when following the keto diet, and for how long?
While on the keto diet, you should avoid high-carb foods such as bread, pasta, rice, sugary snacks, and most fruits. The duration of this restriction typically lasts until your body reaches a state of ketosis, which can take anywhere from a few days to a couple of weeks. After achieving ketosis, you can consider reintroducing certain low-carb foods in moderation, depending on your personal goals and how your body reacts to the changes.
References
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5781288/
- https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/keto-diet-101
- https://www.cdc.gov/healthyweight/healthy_eating/dietary_guidelines.html
- https://www.webmd.com/diet/obesity/features/keto-diet-weight-loss#1
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/nutrition-and-healthy-eating/expert-answers/keto-diet/faq-20452629
- https://www.hhs.gov/healthcare/about-the-hhs/initiatives/healthy-people/index.html
- https://www.theguardian.com/lifeandstyle/2020/jan/11/keto-diet-explained-what-is-it-benefits-risks
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0899900718302159

